Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Stem Cells. Mar 26, 2015; 7(2): 266-280
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.266
Published online Mar 26, 2015. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.266
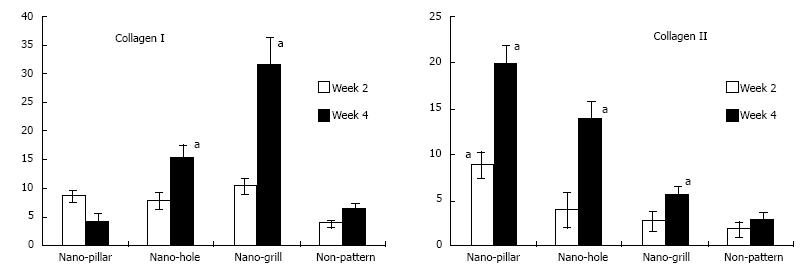
Figure 7 The effect of nano-patterned surfaces on the expression of cartilaginous genes.
Real time polymerase chain reaction was used to analyse mRNA expression levels of cartilaginous genes at week 2, 4 or 6 of chondrogenic differentiation, which was normalised to their respective glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression and expressed as fold changes relative to undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. n = 3 per group, mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 which was considered statistically significant compared to non-patterned surface[55].
- Citation: Salmasi S, Kalaskar DM, Yoon WW, Blunn GW, Seifalian AM. Role of nanotopography in the development of tissue engineered 3D organs and tissues using mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2015; 7(2): 266-280
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v7/i2/266.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v7.i2.266