Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Stem Cells. Nov 26, 2014; 6(5): 614-619
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.614
Published online Nov 26, 2014. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.614
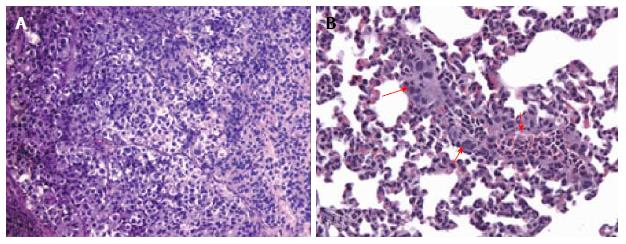
Figure 1 Histological images showing subcutaneous thyroid cancer mouse model.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin stained microphotograph of tumor xenografts engrafted human thyroid cancer cell line (K1) with adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) (× 100); B: HE microphotograph of lung metastasis (red arrows) in the group transplanted with K1 cells and ASCs (× 200). Methods of image acquisition: Tumor and organs removed from mouse, photographed, and stored in 10% neutral buffered formalin for paraffin sectioning and HE staining. Tumor tissue were sectioned and stained with HE[28].
- Citation: Bhatia P, Tsumagari K, Abd Elmageed ZY, Friedlander P, Buell JF, Kandil E. Stem cell biology in thyroid cancer: Insights for novel therapies. World J Stem Cells 2014; 6(5): 614-619
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v6/i5/614.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i5.614