Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Stem Cells. Feb 26, 2011; 3(2): 9-18
Published online Feb 26, 2011. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v3.i2.9
Published online Feb 26, 2011. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v3.i2.9
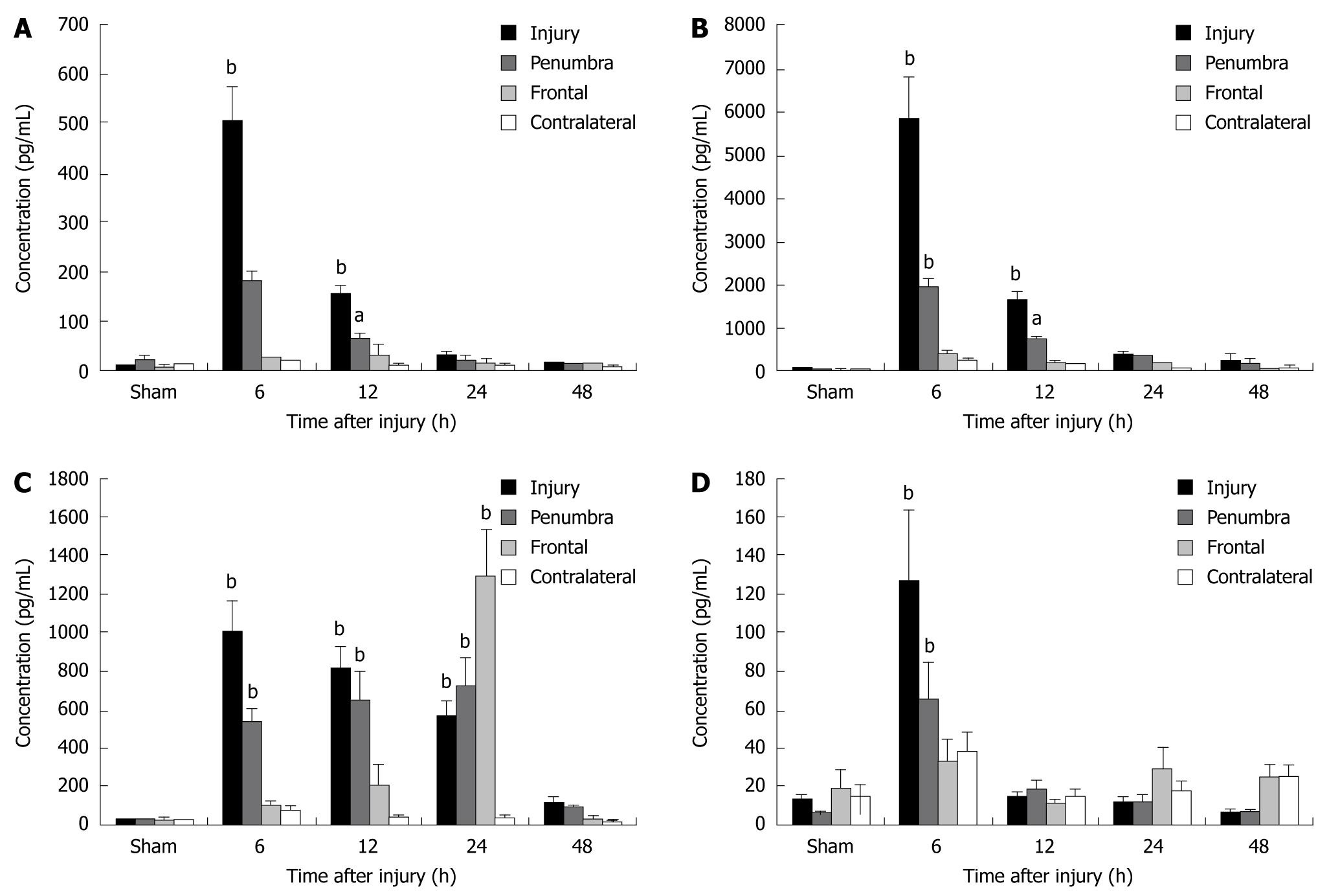
Figure 1 Elevated intracerebral cytokines identified in specific areas and at specific time points relative to the traumatic brain injury.
The proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1α (A), IL-1β (B), IL-6 (C), and tumor necrosis factor-α (D) were significantly elevated 6 h after CCI in the injury and penumbral regions when compared with sham animals (bP < 0.01 for all). IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-6 remained elevated through 12, 12 and 24 h, respectively (bP < 0.01 or aP < 0.05). In the frontal area, IL-6 was significantly increased at 24 h (33- to 50-fold; P < 0.01; Dunnett's test), but not at 6 or 12 h after traumatic brain injury. Reproduced with permission[22].
-
Citation: Walker PA, Letourneau PA, Bedi S, Shah SK, Jimenez F, Jr CSC. Progenitor cells as remote "bioreactors": Neuroprotection
via modulation of the systemic inflammatory response. World J Stem Cells 2011; 3(2): 9-18 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v3/i2/9.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v3.i2.9