Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Stem Cells. May 26, 2023; 15(5): 438-452
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.438
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.438
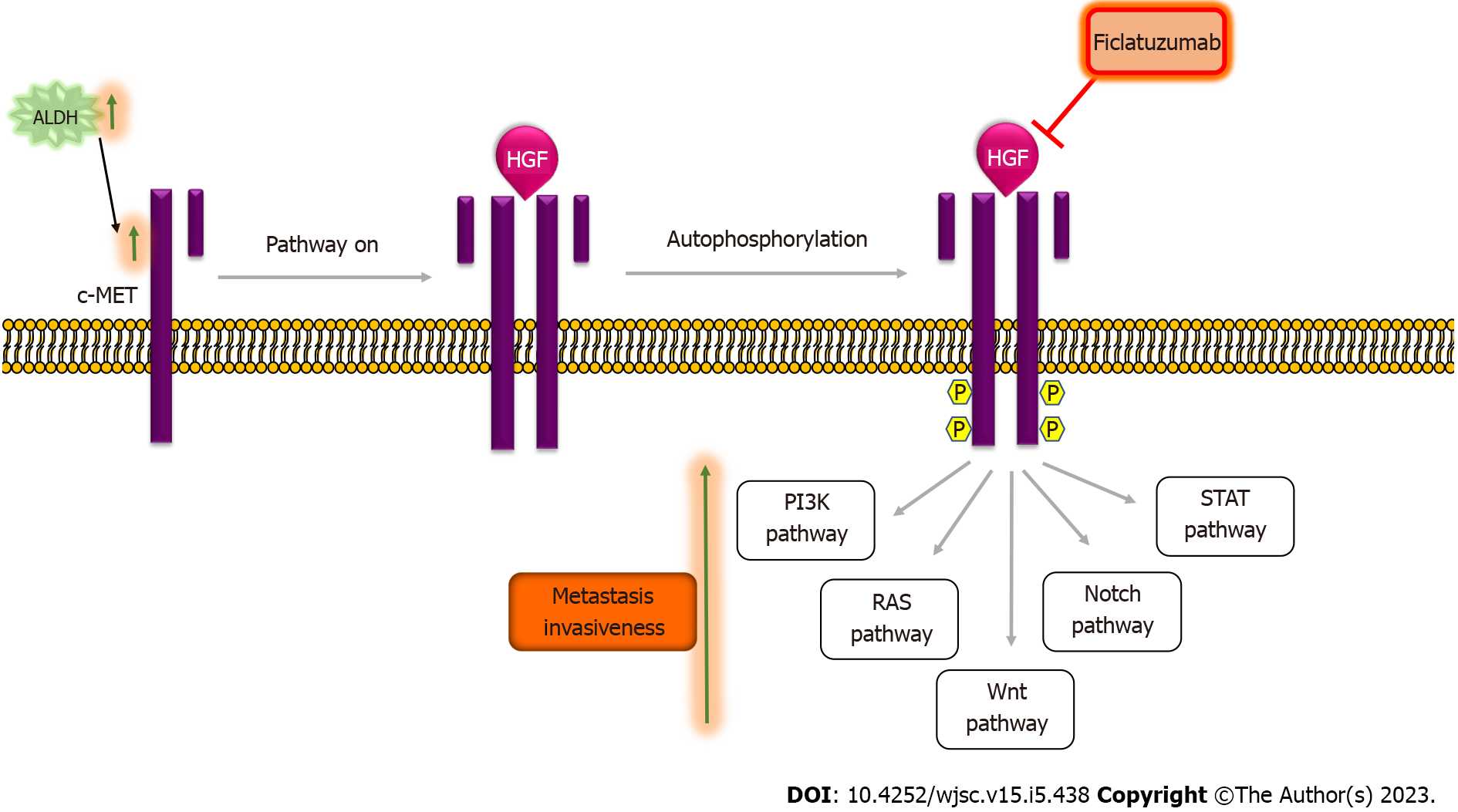
Figure 4 The HGF/c-MET signaling pathway and cancer stemness.
In the absence of the HGF ligand, the HGF/c-MET pathway remains inactivated. The binding of the HGF ligand to the c-MET kinase receptor results in the dimerization of two subunits that further leads to auto-phosphorylation of the tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor creating a docking site for adaptor proteins, which regulate pathways, such as PI3K, RAS, Wnt, Notch and STAT pathway. Transcriptional levels of c-MET were high in ALDHhigh cells[70]. Activation of c-MET results in an increase in invasiveness and metastasis in vitro as well as in vivo[73,74]. Ficlatuzumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting HGF used to therapeutically target the HGF/c-met pathway. ALDH: Aldehyde dehydrogenase; Ficlatuzumab: HGF/c-MET pathway inhibitor.
- Citation: Joshi P, Waghmare S. Molecular signaling in cancer stem cells of tongue squamous cell carcinoma: Therapeutic implications and challenges. World J Stem Cells 2023; 15(5): 438-452
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v15/i5/438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.438