Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2021; 13(6): 568-593
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.568
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.568
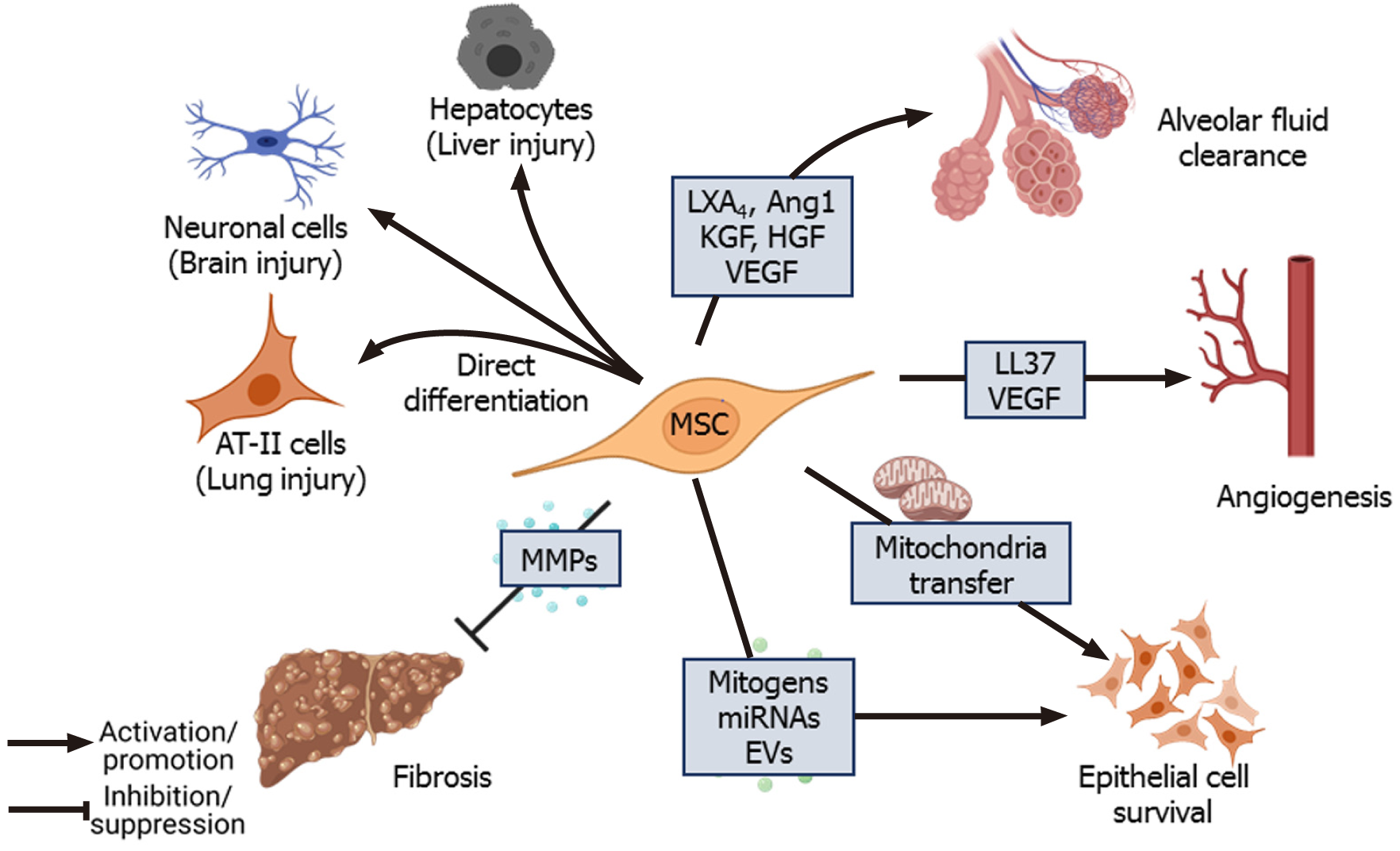
Figure 2 Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) secrete various paracrine factors and chemokines to reduce inflammation at the site of injury by inhibiting infiltration of neutrophils, pro-inflammatory monocytes, and maturation of dendritic cells[39,62,219]. MSCs promote anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype in macrophages, improve phagocytic ability and increase their survival via mitochondrial transfer[12,43-45,48]. MSCs under inflammatory conditions inhibit T-cell proliferation via secretion of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and PD-L2[54]. MSCs induce a “tolerogenic” phenotype in monocytes and promote migration of regulatory T cells to the site of infection[58,60]. Ang1: Angiopoietin-1; EVs: Extracellular vesicles; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; KGF: Keratinocyte growth factor; LXA: LipoxinA4; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Sharma A, Chakraborty A, Jaganathan BG. Review of the potential of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of infectious diseases. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(6): 568-593
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i6/568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.568