Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2021; 13(6): 568-593
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.568
Published online Jun 26, 2021. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.568
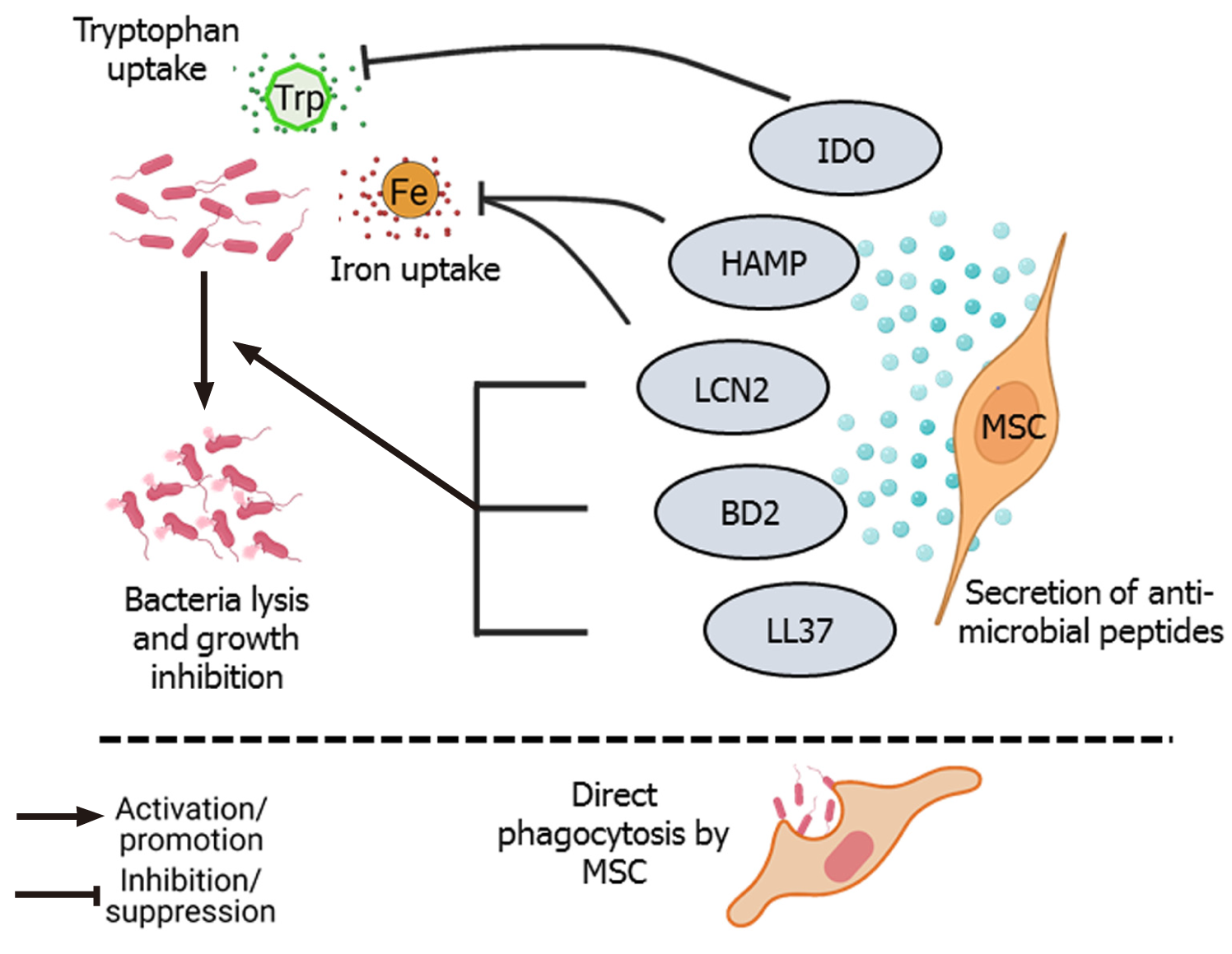
Figure 1 Direct bacterial lysis and phagocytosis.
Secretion of antimicrobial peptides such as LL-37, β-defensin 2 (BD2), lipocalin 2 (LCN2), hepcidin antimicrobial peptide (HAMP), and indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have bactericidal effects[23,24,30,31]. LCN2 and HAMP inhibit iron (Fe) uptake by bacterial cells, and IDO inhibits the uptake of the essential amino acid tryptophan (Trp), leading to growth inhibition and death of bacterial cells[27,29]. MSCs can also directly phagocytose bacteria[32].
- Citation: Sharma A, Chakraborty A, Jaganathan BG. Review of the potential of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of infectious diseases. World J Stem Cells 2021; 13(6): 568-593
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v13/i6/568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v13.i6.568