Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Stem Cells. Dec 26, 2018; 10(12): 196-211
Published online Dec 26, 2018. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i12.196
Published online Dec 26, 2018. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i12.196
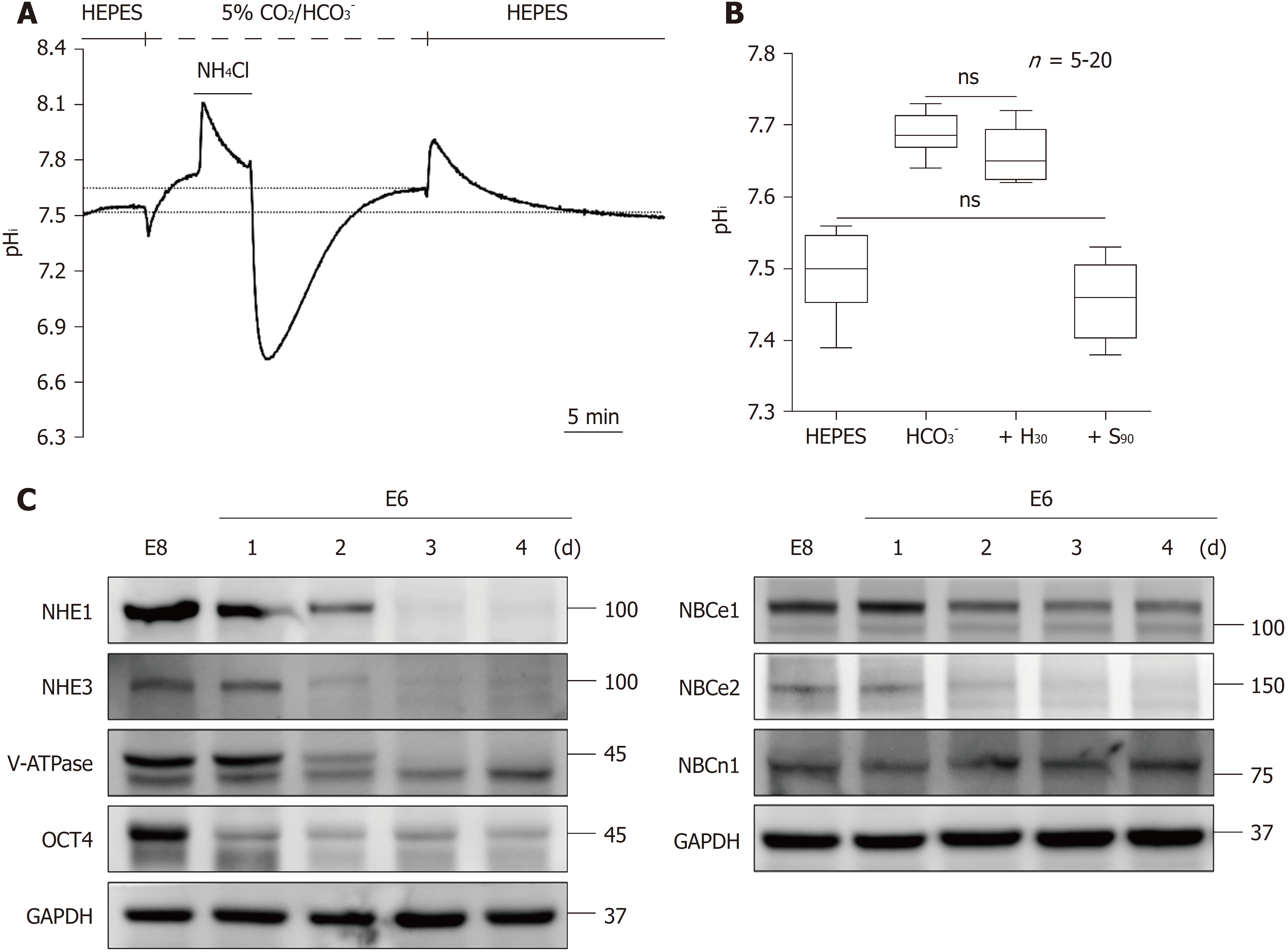
Figure 5 Steady-state pHi in HEPES and 5% CO2/HCO3--buffered solution and the change in the expression of pHi regulators during the loss of pluripotency in human induced pluripotent stem cells.
A: The resting pHi was a steady-state taken from the completely recovered pHi after intracellular acidification or alkalization. The dotted line indicates the value of the resting pHi; B: The max/min chart of the resting pHi in hiPSCs was collected from A (n = 20) and Figures 4C and D (n = 5). The means of the resting pHi in HEPES and 5% CO2/HCO3--buffered solution were found to be 7.50 ± 0.01 and 7.68 ± 0.01, respectively. After treatment with H30 and S90 in 5% CO2/HCO3--buffered solution, the resting pHi shifted to 7.66 ± 0.02 and 7.46 ± 0.02, respectively; C: Immunoblot analysis of the expression of NHE1, NHE3, V-ATPase, NBCe1, NBCe2, NBCn1 and OCT4 in hiPSCs in different culture media for different days (E8 and E6-1d to E6-4d). The histograms in B display the mean and the min to max values. hiPSCs: Human induced pluripotent stem cells; NHE: The Na+/H+ exchanger; NBC: The Na+/HCO3- cotransporter; V-ATPase: Vacuolar-ATPase.
- Citation: Chao SC, Wu GJ, Huang SF, Dai NT, Huang HK, Chou MF, Tsai YT, Lee SP, Loh SH. Functional and molecular mechanism of intracellular pH regulation in human inducible pluripotent stem cells. World J Stem Cells 2018; 10(12): 196-211
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v10/i12/196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v10.i12.196