Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2023; 29(34): 5038-5053
Published online Sep 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i34.5038
Published online Sep 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i34.5038
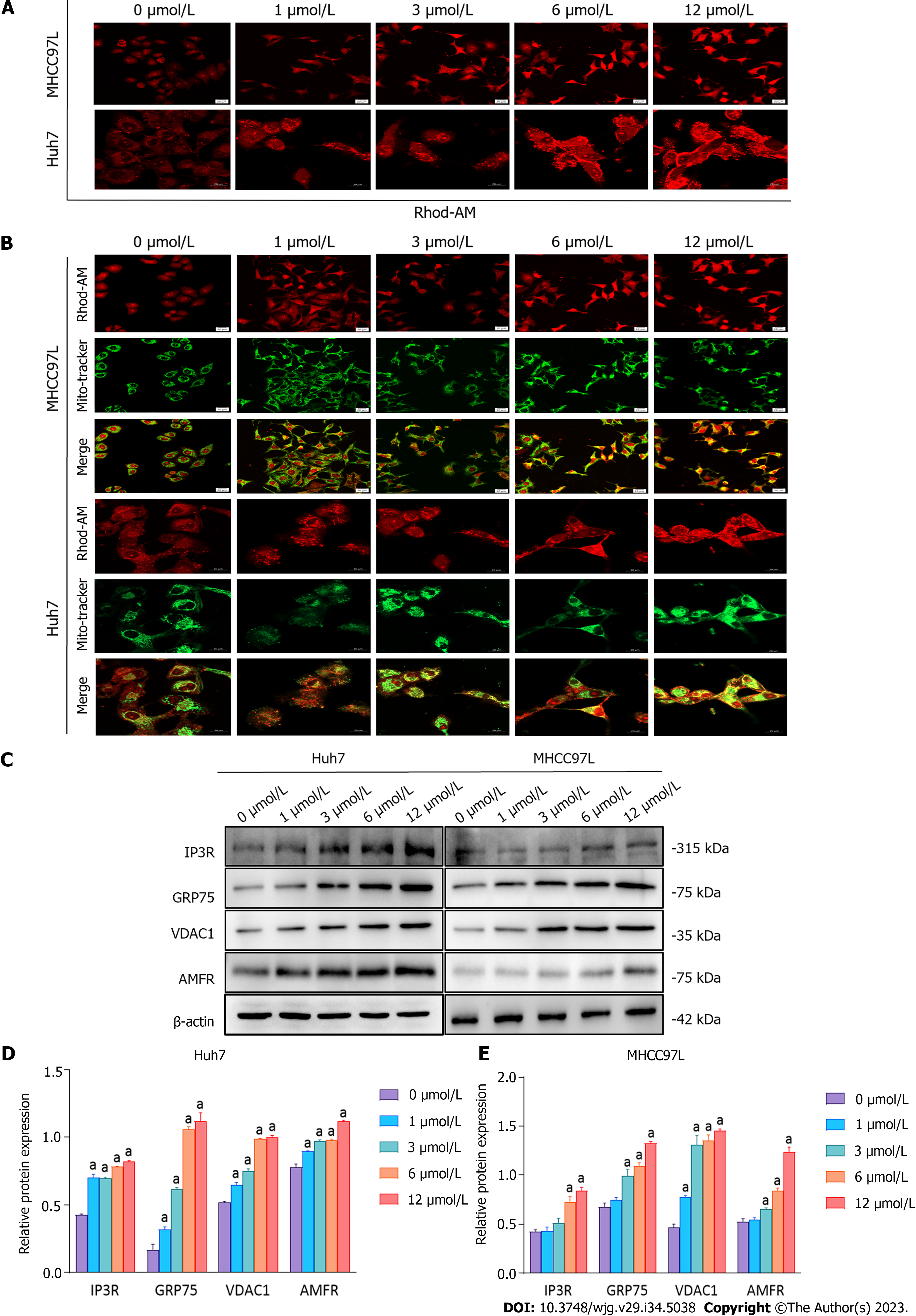
Figure 5 Impact of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid treatment on Ca2+ homeostasis and the expression of autocrine motility factor receptor and proteins related to mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum contact sites in Huh7 and MHCC97L cells.
A: Huh7 and MHCC97L cells were exposed to 0, 1, 3, 6, and 12 μmol/L suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) for 48 h and stained with Rhod-2 AM. The cells were observed under a confocal microscope (× 400 magnification); B: Huh7 and MHCC97L cells were exposed to 0, 1, 3, 6, and 12 μmol/L SAHA for 48 h and simultaneously stained with Mito-Tracker Green and Rhod-2 AM Red. The cells were observed under a confocal microscope (× 400 magnification). The scale is 100 μm; C-E: Representative western blot images showed the expression of inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor type 1, glucose-regulated protein 75, voltage-dependent anion channel 1, and autocrine motility factor receptor in Huh7 and MHCC97L cells treated with SAHA for 48 h. Relative protein expression levels were normalized to β-actin. Data are exhibited as mean ± standard deviation. aP < 0.05 vs 0 μmol/L group (n = 3). AMFR: Autocrine motility factor receptor; IP3R1: Inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptor type 1; GRP75: Glucose-regulated protein 75; VDAC1: Voltage-dependent anion channel 1.
- Citation: Li JY, Tian T, Han B, Yang T, Guo YX, Wu JY, Chen YS, Yang Q, Xie RJ. Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid upregulates reticulophagy receptor expression and promotes cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(34): 5038-5053
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i34/5038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i34.5038