Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2023; 29(13): 1942-1954
Published online Apr 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i13.1942
Published online Apr 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i13.1942
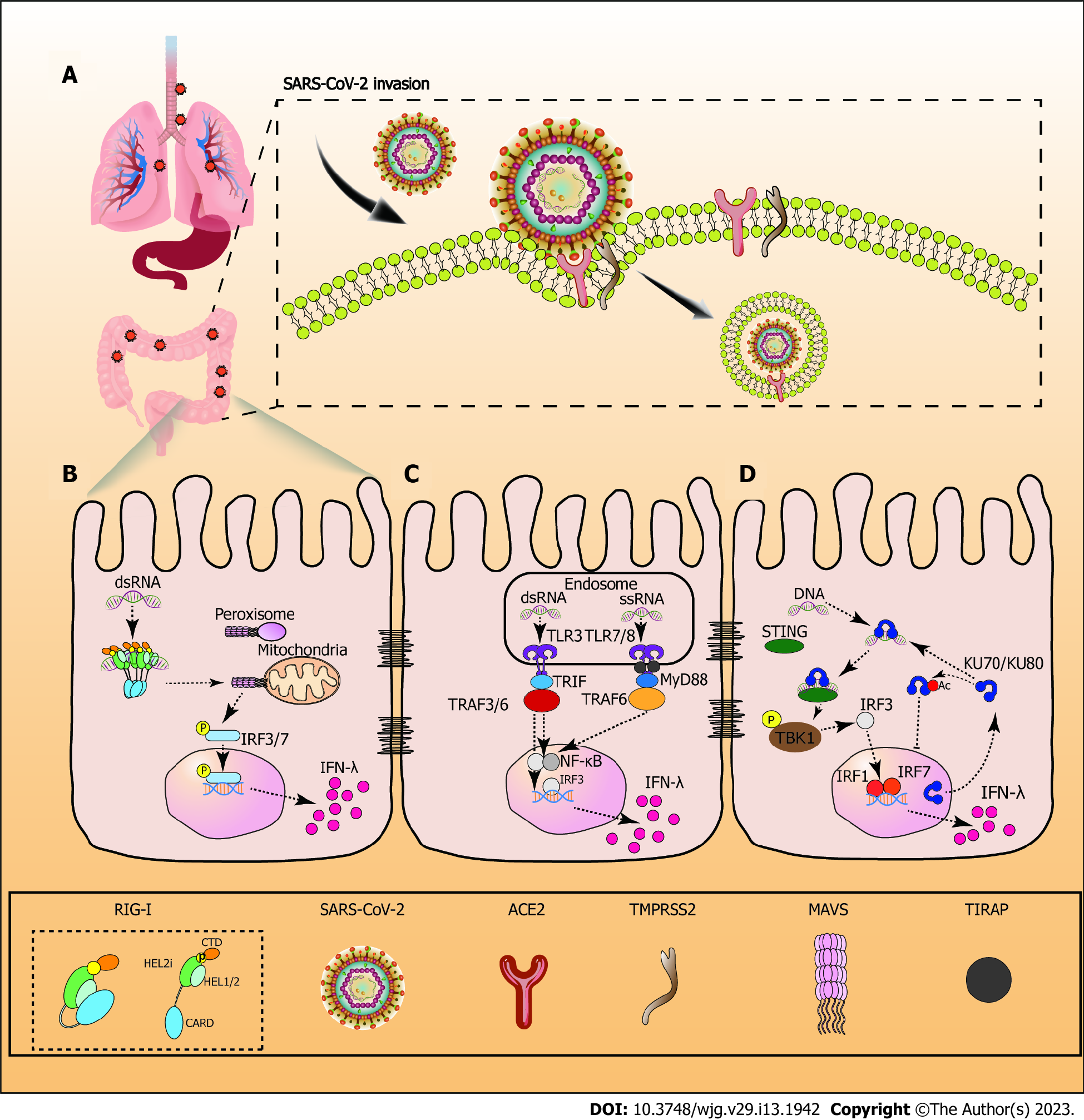
Figure 1 Infection mechanism of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 and retinotic acid-inducible gene 1.
A: Process of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 invasion in the gastrointestinal tract; B: Retinotic acid-inducible gene 1 (RIG-I) contains a pair of caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), an ATPase motor domain (Helicase domain) that consists of two RecA domains (Hel1 and Hel2), and an alpha-helical insertion domain (Hel2i) connected via a Pincer motif (P) and a C-terminal domain. When RIG-I is in the inactivated state it clasps the CARDs against the surface of Hel2i. Once engaged with viral RNA, these pathogen RNAs trigger conformational changes that anchor the RNA tightly inside the RIG-I receptor and trigger the release of the CARDs[91]. Activated RIG-I interacts with mitochondrial antiviral signaling proteins to recruit phosphorylated interferon regulatory factor (IRF)3/7 in the nucleus, subsequently inducing interferon-λ (IFN-λ) production; C: Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3 interacts with dsRNA at opposite ends of the horseshoe ring in the endosome. TLR3 recruited TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF) via the myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) independent pathway. TRIF then recruits and activates the tumour necrosis factor receptor associated factor (TRAF) 3/6, inducing the recruitment of IRF3 and nuclear factor kB (NF-κB) in the nucleus. After TLR7/8 recognizes viral ssRNA in the endosome, the receptor-proximal membrane protein TIRAP detects the dimerized TIR domain of TLR7/8, and stimulates MyD88 to interact with it. MyD88 subsequently recruits TRAF6, leading to the recruitment of IRF3 and NF-κB in the nucleus. Once IRF3 binds to the promoter, IFN-λ gene expression is initiated[92,93]; D: Ku80 is co-localized with Ku70. Ku70 translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and recognizes cytosolic viral DNA. Subsequently, Ku70 with the DNA interacts with stimulator of interferon genes to phosphorylate TANK-binding kinase 1. Finally, IRF3 is activated, and produces the strong expression of IRF1and IRF7, which induce IFN-λ expression. Acetylation increases Ku70 accumulation in the cytoplasm and promotes DNA-mediated Ku70-dependent IFN-λ1 induction[94]. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; IRF3/7: Interferon regulatory factor 3/7; IFN-λ: Interferon-λ; TRAF: Tumour necrosis factor receptor associated factor; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TRIF: TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kB; TBK1: TANK-binding kinase 1; STING: Stimulator of interferon genes; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response 88.
- Citation: Pan YY, Wang LC, Yang F, Yu M. Interferon-lambda: New role in intestinal symptoms of COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(13): 1942-1954
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i13/1942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i13.1942