Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2022; 28(3): 275-289
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i3.275
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i3.275
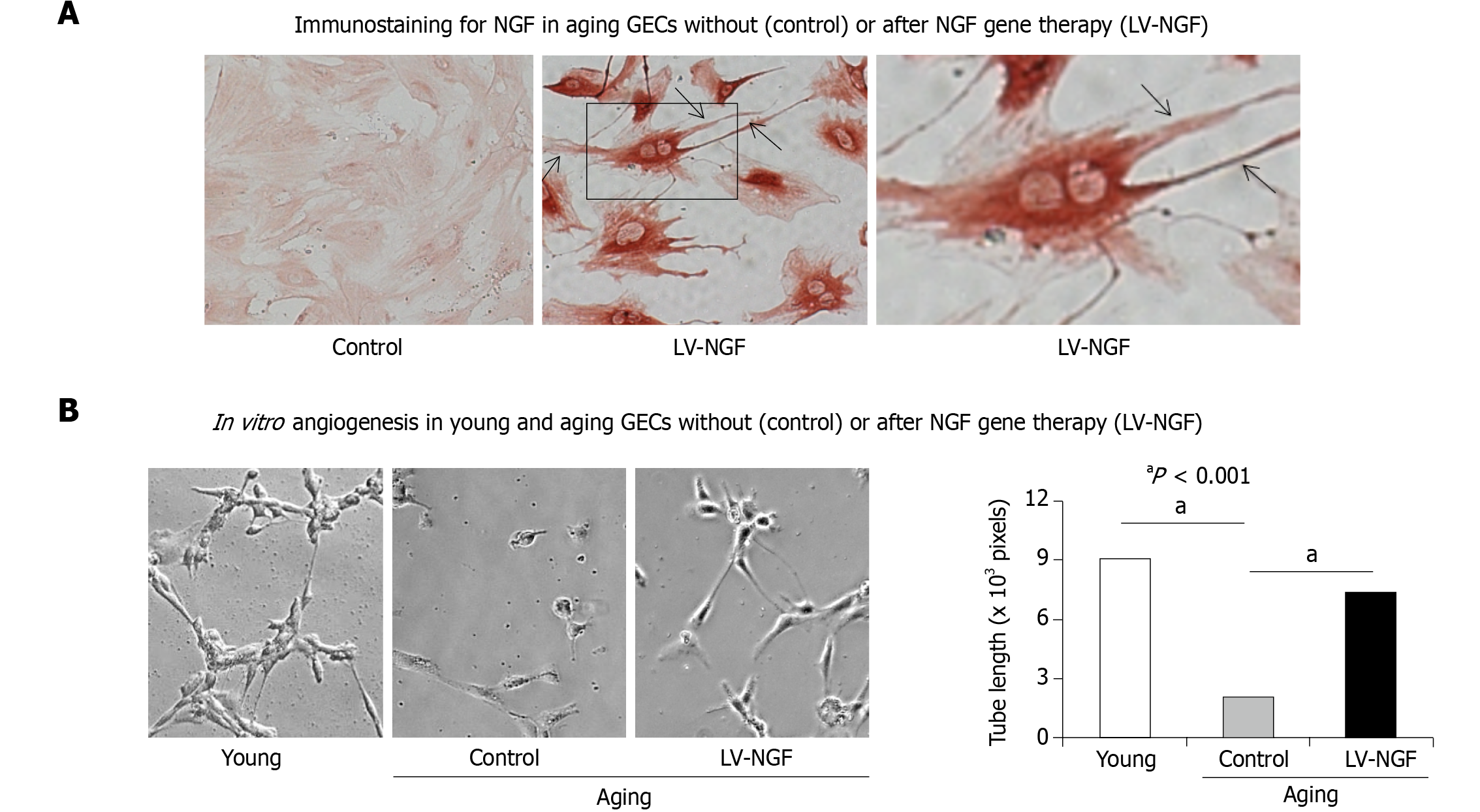
Figure 4 Nerve growth factor gene therapy increases nerve growth factor expression and reverses impaired in vitro angiogenesis in aging gastric endothelial cells.
A: Nerve growth factor (NGF) gene therapy of aging Gastric endothelial cells (GECs) using lentiviral-NGF (LV-NGF) induced NGF expression (brown staining) and extensive, long filopodia (arrows) reflecting a change in these cells to an angiogenic phenotype; aging GECs without gene therapy (negative controls) have minimal NGF expression and lack filopodia; B: NGF gene therapy with LV-NGF resulted in 3.7-fold increased in vitro angiogenesis at 6 h in aging GECs vs negative controls (control). Panels are representative images of capillary-like tube formation. Original magnification: × 200. Data are means ± SD (n = 6). (aP < 0.001). NGF: Nerve growth factor; GEC: Gastric endothelial cells; LV: Lentiviral. Reproduced with permission from reference[20], which is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
- Citation: Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A. Endothelial cells and blood vessels are major targets for COVID-19-induced tissue injury and spreading to various organs. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(3): 275-289
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i3/275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i3.275