Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2022; 28(26): 3008-3026
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008
Published online Jul 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008
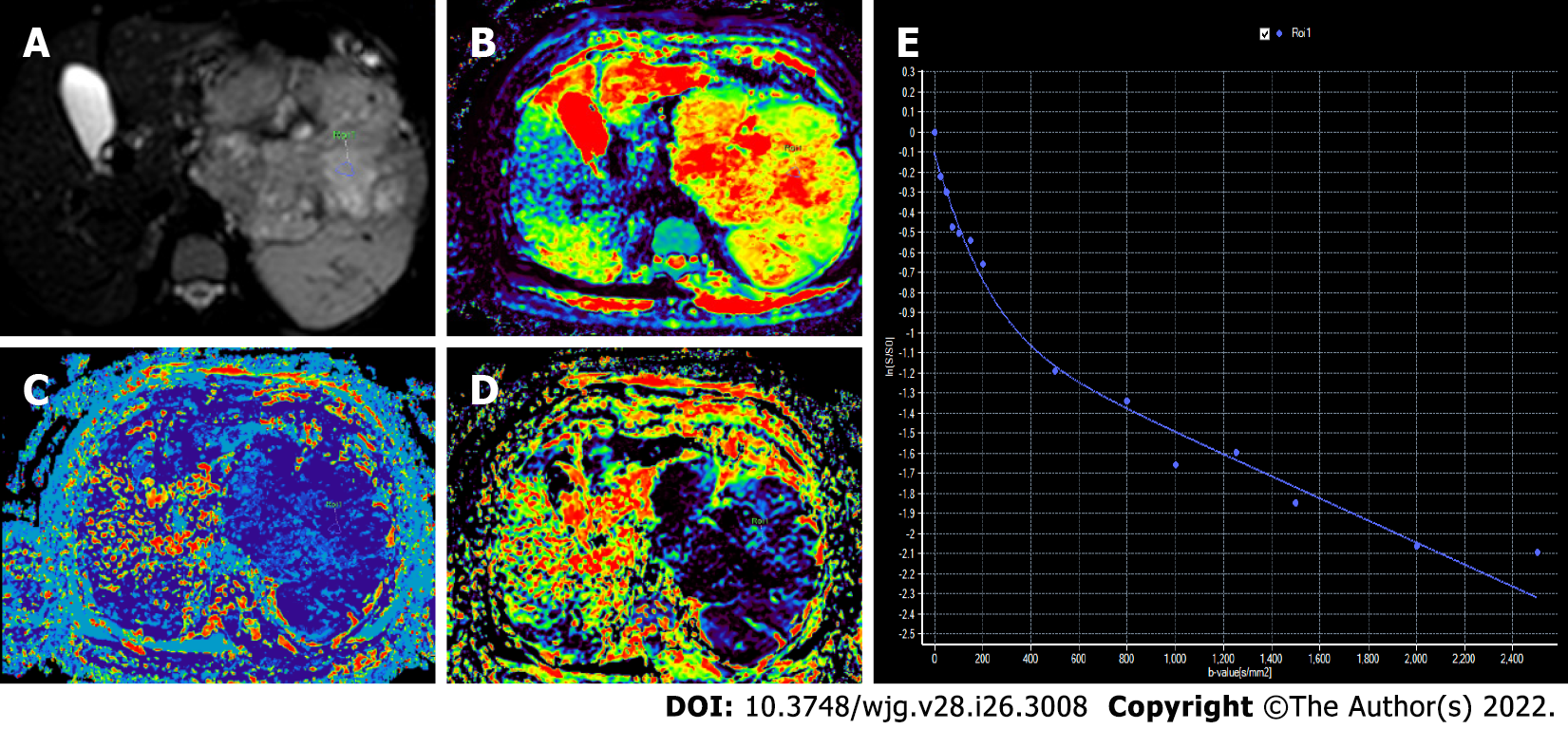
Figure 8 Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in a 67-year-old man with grade 3 pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Axial diffusion weighted image (b = 200 s/mm2) with circular region of interest in the tumor; B: Color-coded diffusion map shows true diffusion coefficient, D = 0.84 × 103 mm2/s; C: Color-coded perfusion map shows pseudodiffusion coefficient, D* = 5.01 × 103 mm2/s); D: Color-coded perfusion fraction map shows a value, f = 4.5%; E: Signal decay curve shows steeper decay at low b values and continued fall at higher b values [in comparison to grade 1 pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm (PNEN) (Figure 7), true diffusion coefficient is lower in grade 3 PNENs].
- Citation: Ramachandran A, Madhusudhan KS. Advances in the imaging of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(26): 3008-3026
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i26/3008.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i26.3008