Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2021; 27(9): 794-814
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.794
Published online Mar 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.794
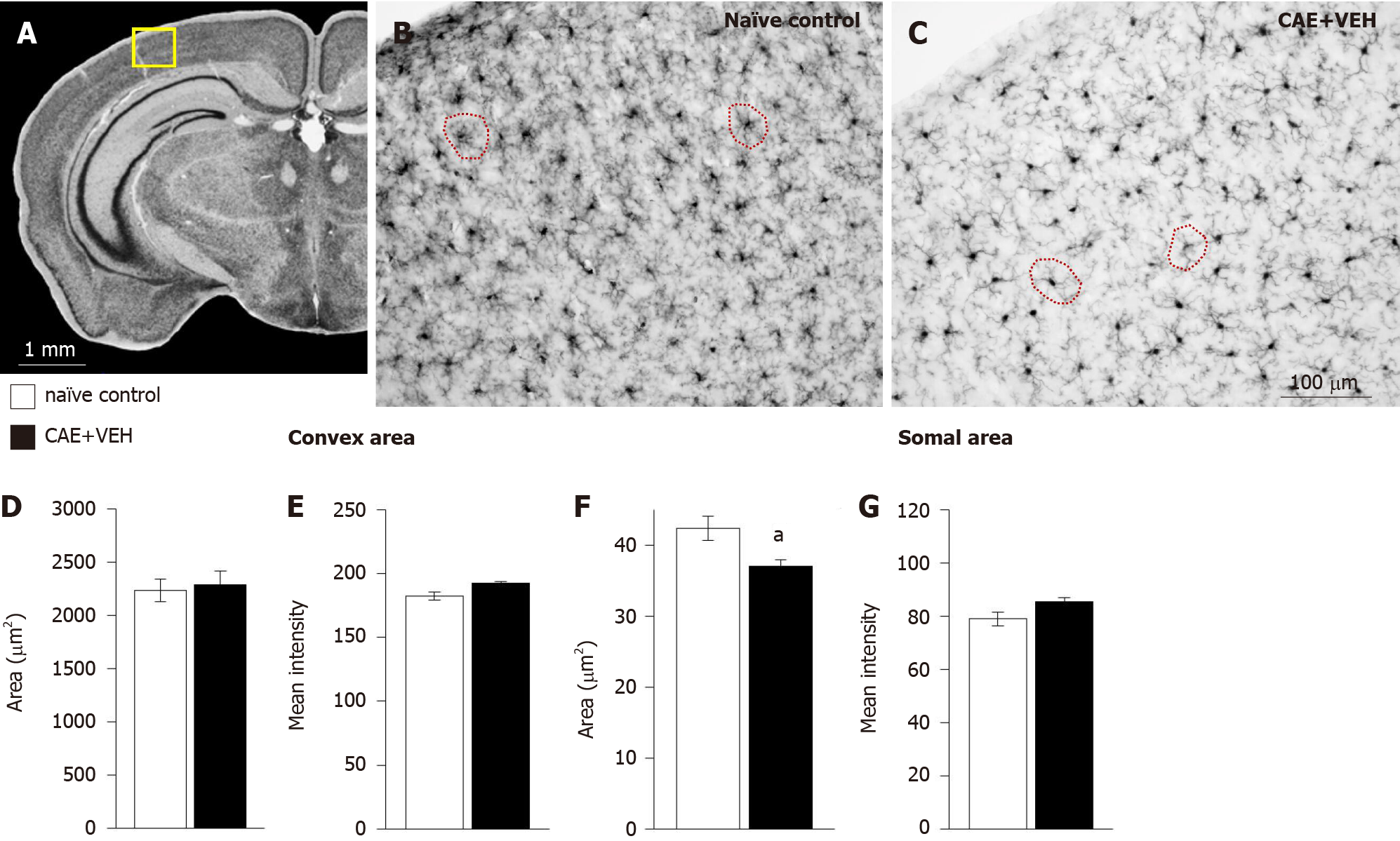
Figure 8 Microglia in the primary somatosensory cortex of mice with caerulein-induced pancreatitis were similar to those from controls.
A: The analyzed area is outlined in yellow in an overview of the mouse brain at bregma -2.18 mm, interaural 1.62 mm[50,51]. B-E: Microglia in (B) naïve control and (C) caerulein- (CAE) induced pancreatitis mice had (D) similar convex areas and (E) staining intensity for ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba1); F and G: In fact, their somal areas were significantly decreased in animals with CAE-induced pancreatitis compared to naïve mice, and their Iba1 staining intensity was not different. Naïve control n = 4, CAE + VEH n = 5, aP < 0.05 Student’s t-test. CAE: Caerulein; VEH: Vehicle.
- Citation: McIlwrath SL, Starr ME, High AE, Saito H, Westlund KN. Effect of acetyl-L-carnitine on hypersensitivity in acute recurrent caerulein-induced pancreatitis and microglial activation along the brain’s pain circuitry. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(9): 794-814
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i9/794.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i9.794