Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2021; 27(46): 7894-7908
Published online Dec 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i46.7894
Published online Dec 14, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i46.7894
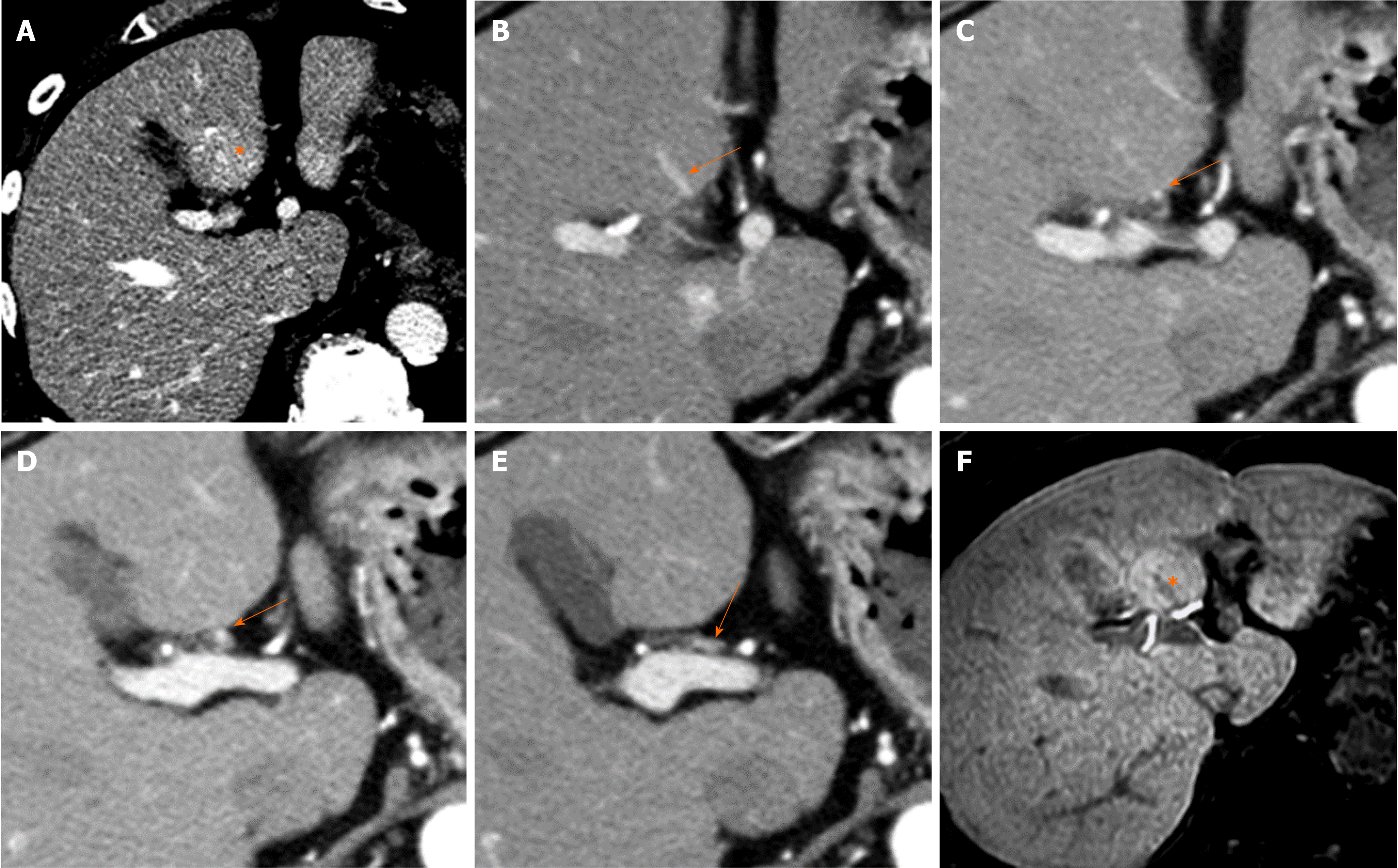
Figure 11 Focal hyperplastic change in posterior aspect of segment IV (70th male).
A: On the portal phase contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT) image, focal hyper-attenuation area is observed in the posterior aspect of segment IV of the liver (*), which is not detected on both pre-contrast CT and equilibrium phase contrast enhanced CT (images are not shown). This is hypervascular pseudolesion observed in the area of aberrant right gastric venous drainage to the liver. B-E: On sequential images of arterial phase contrast enhanced CT, aberrant right gastric vein directly entering to the posterior aspect of segment IV of the liver is well opacified (arrows). F: On hepatobiliary phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, slightly hyper-intensity area is observed in the same place of focal hyper-attenuation area observed in the portal phase contrast enhanced CT image (*), which represents focal hyperplasetic change of the liver in aberrant right gastric venous drainage area in the posterior aspect of segment IV.
- Citation: Kobayashi S. Hepatic pseudolesions caused by alterations in intrahepatic hemodynamics. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(46): 7894-7908
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i46/7894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i46.7894