Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2021; 27(41): 7025-7040
Published online Nov 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7025
Published online Nov 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7025
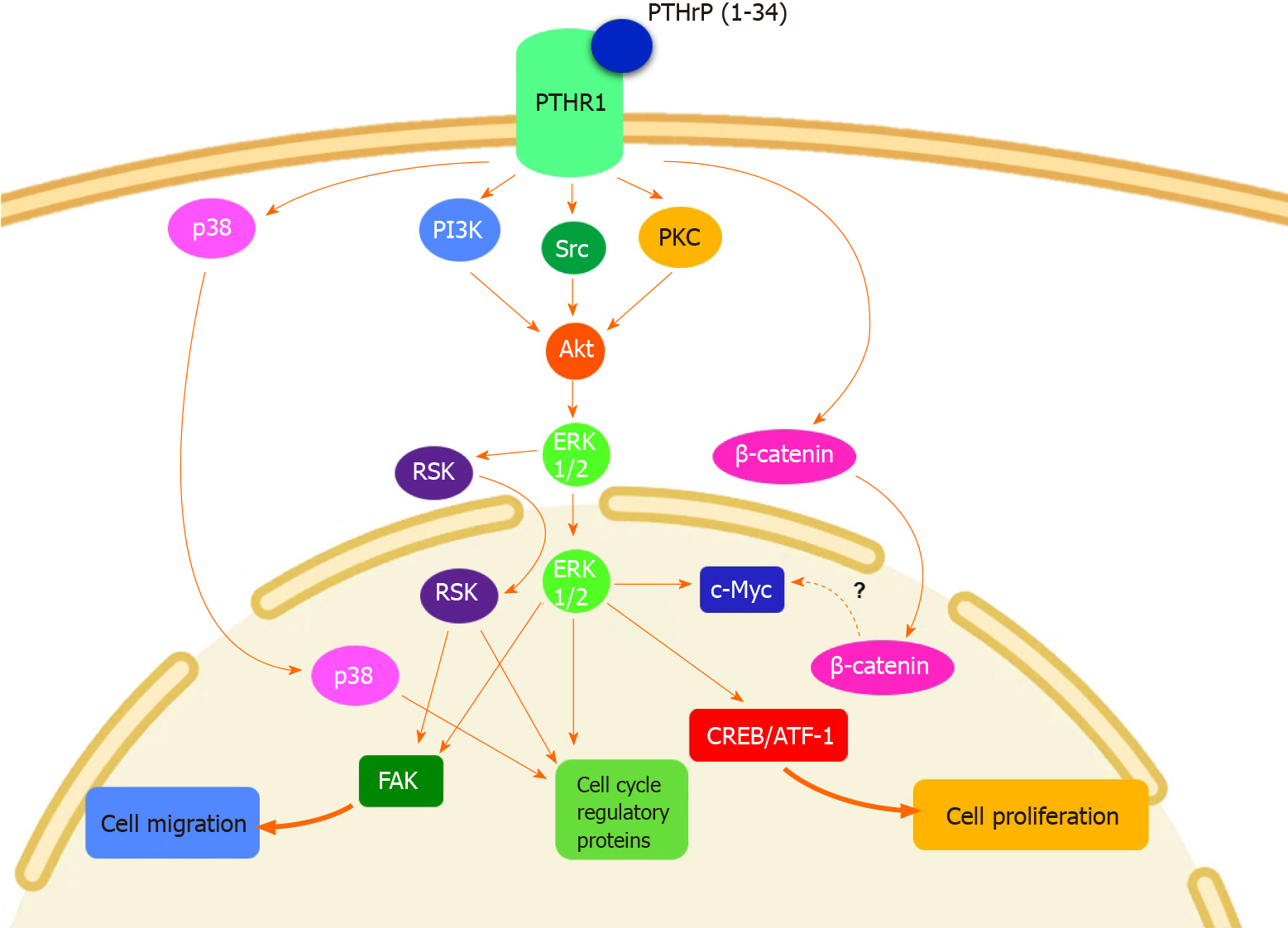
Figure 2 Molecular mechanisms involved in parathyroid hormone-related peptide effects on colorectal cancer cells.
Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) induces cell cycle progression and proliferation of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells through non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src (Src), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and p38, both members of the mitogen activated protein kinases family (MAPK), PI3K/protein kinase B (Akt), p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) and β-catenin pathways. This cytokine also promotes CRC cell migration and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) protein expression through ERK/RSK signaling pathway[37-40]. This figure is original for this work and shows the results published in Calvo et al[37], Martín et al[38], Martín et al[39], and Calvo et al[40]. ATF-1: Activating transcription factor 1; CREB: cAMP response element binding protein; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase;PKC: Protein kinase C; PTHR1: Parathyroid hormone receptor 1.
- Citation: Novoa Díaz MB, Carriere PM, Martín MJ, Calvo N, Gentili C. Involvement of parathyroid hormone-related peptide in the aggressive phenotype of colorectal cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(41): 7025-7040
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i41/7025.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7025