Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2021; 27(35): 5908-5918
Published online Sep 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i35.5908
Published online Sep 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i35.5908
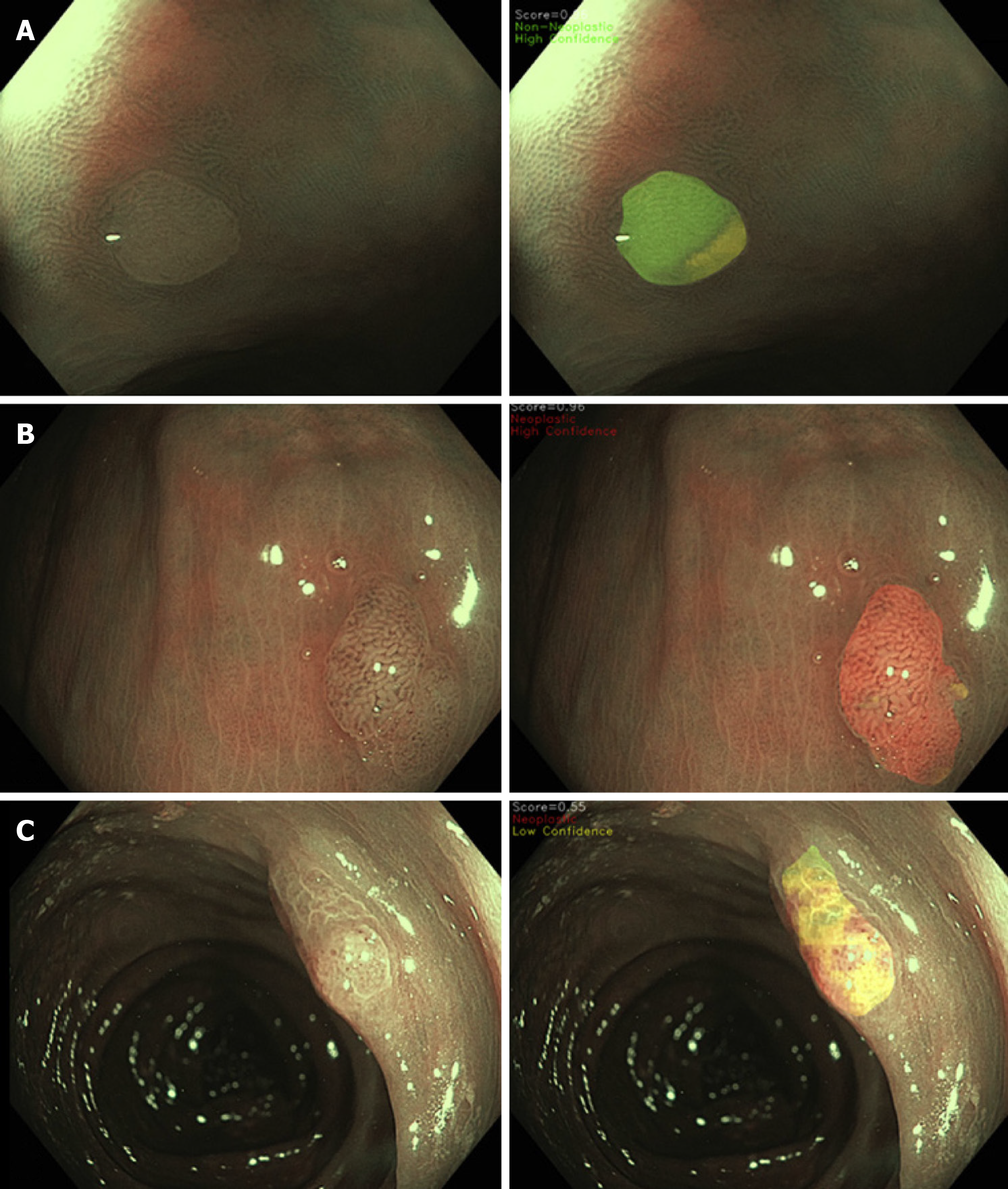
Figure 3 Spatial colour coded histology map which allows the user to visualise the sub-regions of the polyp surface that contributed to the convolutional neural networks’s decision process.
A: Hyperplastic polyps; B: Adenomatous polyps; C: Sessile serrated lesions; Red: High-confidence neoplastic diagnosis; Green: High-confidence non-neoplastic diagnosis; Yellow: Indeterminate or low-confidence diagnosis. Adapted from Ref. [28]. Citation: Rodriguez-Diaz E, Baffy G, Lo WK, Mashimo H, Vidyarthi G, Mohapatra SS, Singh SK. Real-time artificial intelligence-based histologic classification of colorectal polyps with augmented visualization. Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 93: 662-670. Copyright© The Authors 2021. Published by Elsevier.
- Citation: Kader R, Hadjinicolaou AV, Georgiades F, Stoyanov D, Lovat LB. Optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps using convolutional neural networks. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(35): 5908-5918
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i35/5908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i35.5908