Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2020; 26(21): 2729-2739
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2729
Published online Jun 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2729
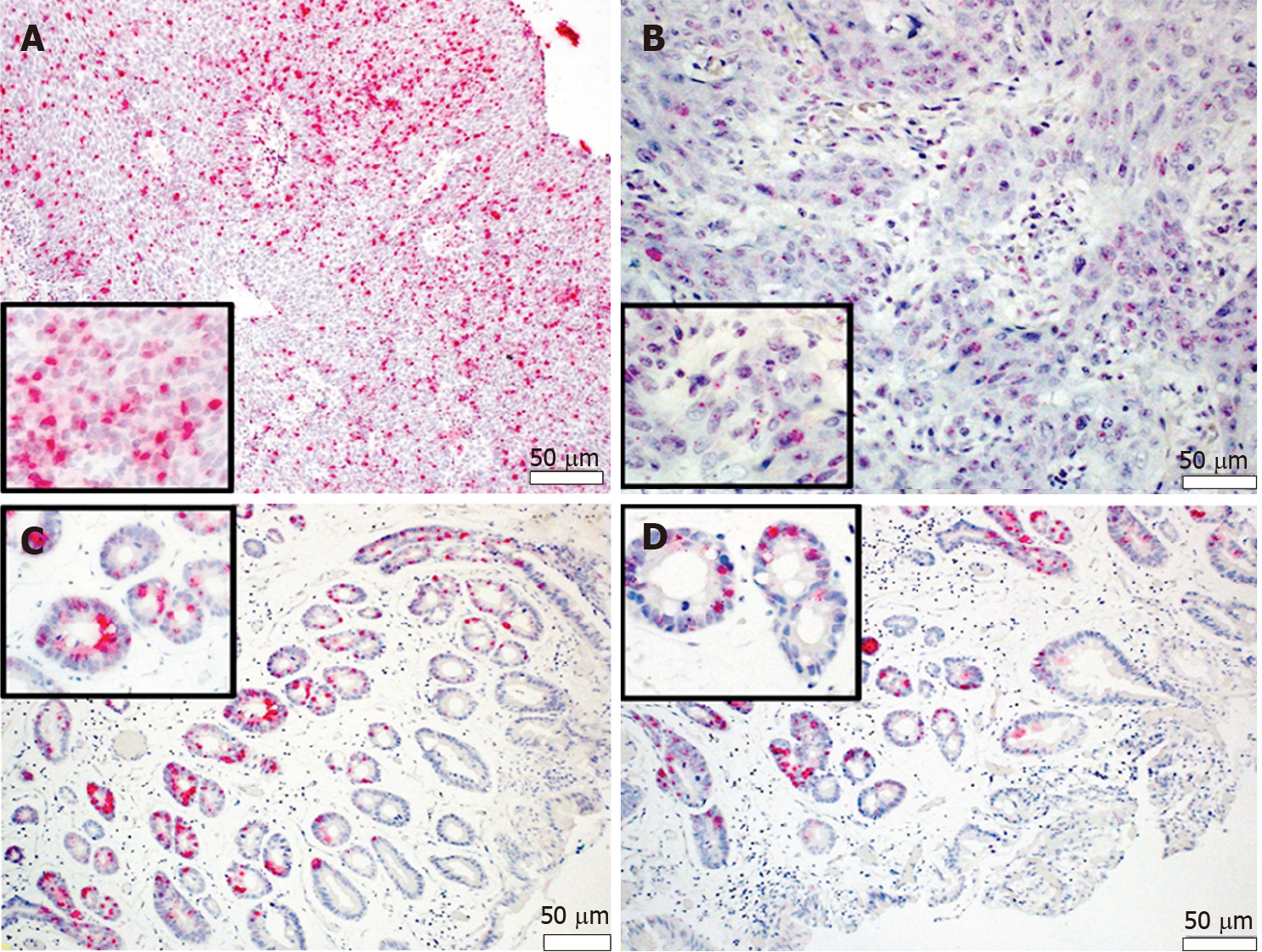
Figure 2 In-situ hybridization detection of transcriptional activity of high-risk human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6/E7 mRNA.
A: HPV16 cervical squamous cell carcinoma; B: HPV16 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; C: HPV16/18 positive EAC; D: Barrett’s esophagus with HGD. (Adapted from: Rajendra et al[71], 2015).
- Citation: Sharma P, Gautam SD, Rajendra S. Importance of investigating high-risk human papillomavirus in lymph node metastasis of esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(21): 2729-2739
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i21/2729.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2729