Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2020; 26(2): 199-218
Published online Jan 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.199
Published online Jan 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.199
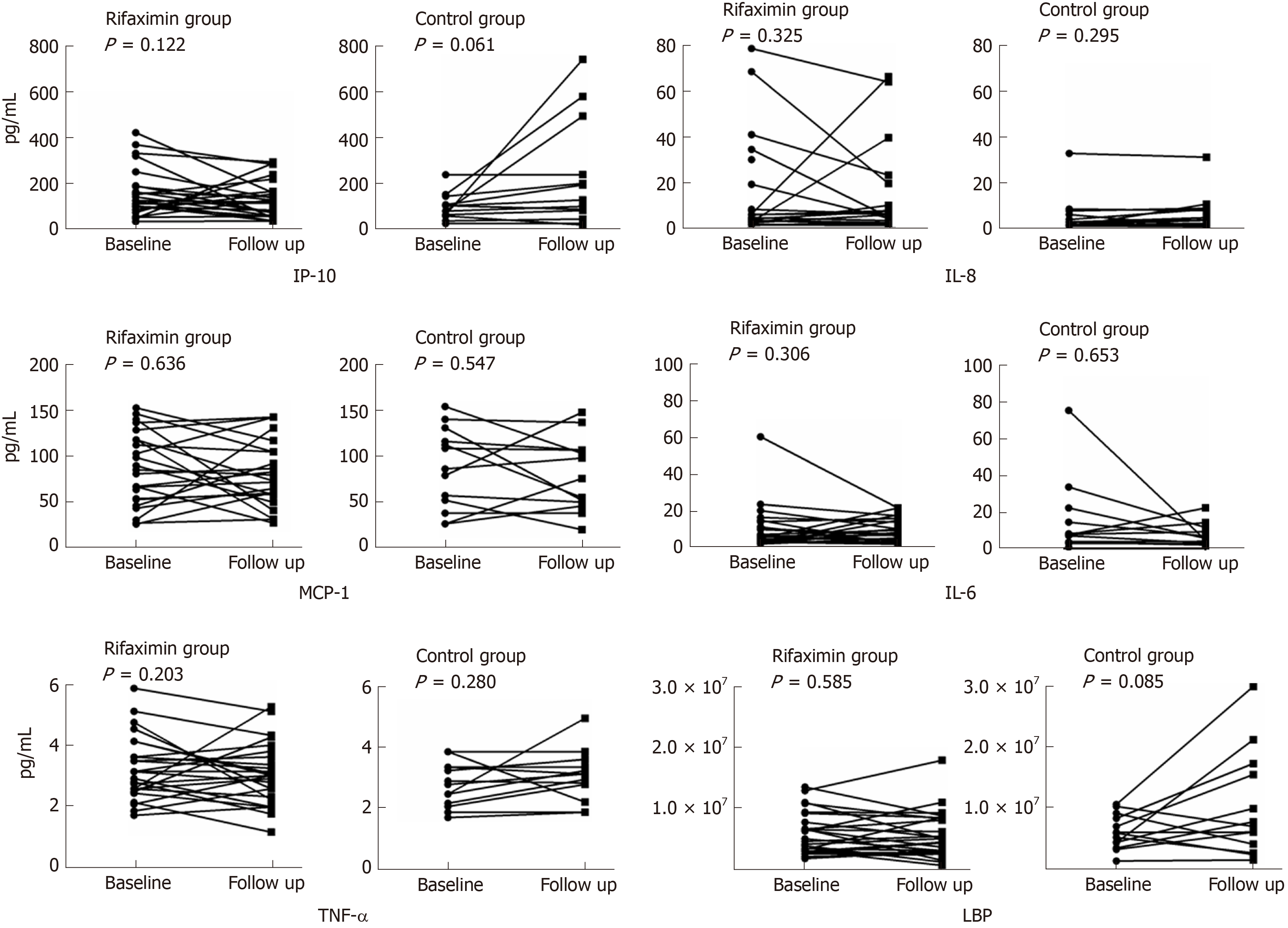
Figure 4 Changes in inflammatory factors and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein after treatment in the two groups.
The concentrations of interferon-inducible protein 10, tumour necrosis factor alpha, and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein showed a downtrend in the rifaximin group but uptrend in the control group, and interferon-inducible protein 10 decreased significantly in the rifaximin compared with the control group (Table 3). IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-8: Interleukin-8; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor alpha; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; LBP: Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; IP-10: Interferon-inducible protein 10.
- Citation: Lv XY, Ding HG, Zheng JF, Fan CL, Li L. Rifaximin improves survival in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: A real-world study. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(2): 199-218
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i2/199.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.199