Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2020; 26(2): 109-133
Published online Jan 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.109
Published online Jan 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.109
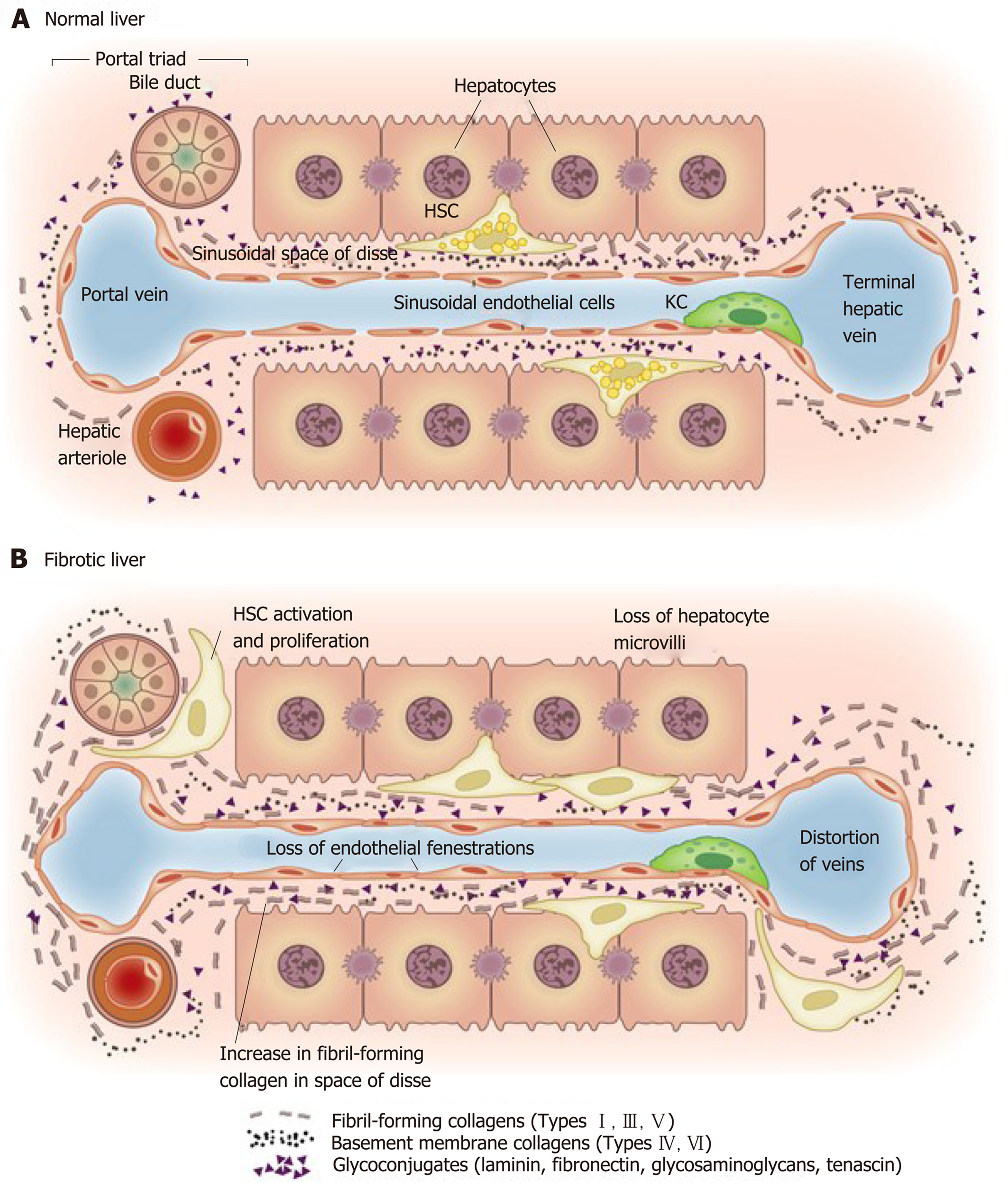
Figure 4 Matrix and cellular alteration in hepatic fibrosis.
Normal liver parenchyma contains epithelial cells (hepatocytes) and nonparenchymal cells: fenestrated sinusoidal endothelium, hepatic stellate cells, and Kupffer cells. A: After injury, the stellate cells become activated and secrete large amounts of extracellular matrix (ECM); B: Deposition of ECM in the space of Disse leads to the loss of both endothelial fenestrations and hepatocyte microvilli. Reproduced with permission from Hernandez-Gea and Friedman[37]. HSC: Hepatic stellate cells; KC: Kupffer cells.
- Citation: Tanwar S, Rhodes F, Srivastava A, Trembling PM, Rosenberg WM. Inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(2): 109-133
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i2/109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i2.109