Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2018; 24(38): 4311-4329
Published online Oct 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i38.4311
Published online Oct 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i38.4311
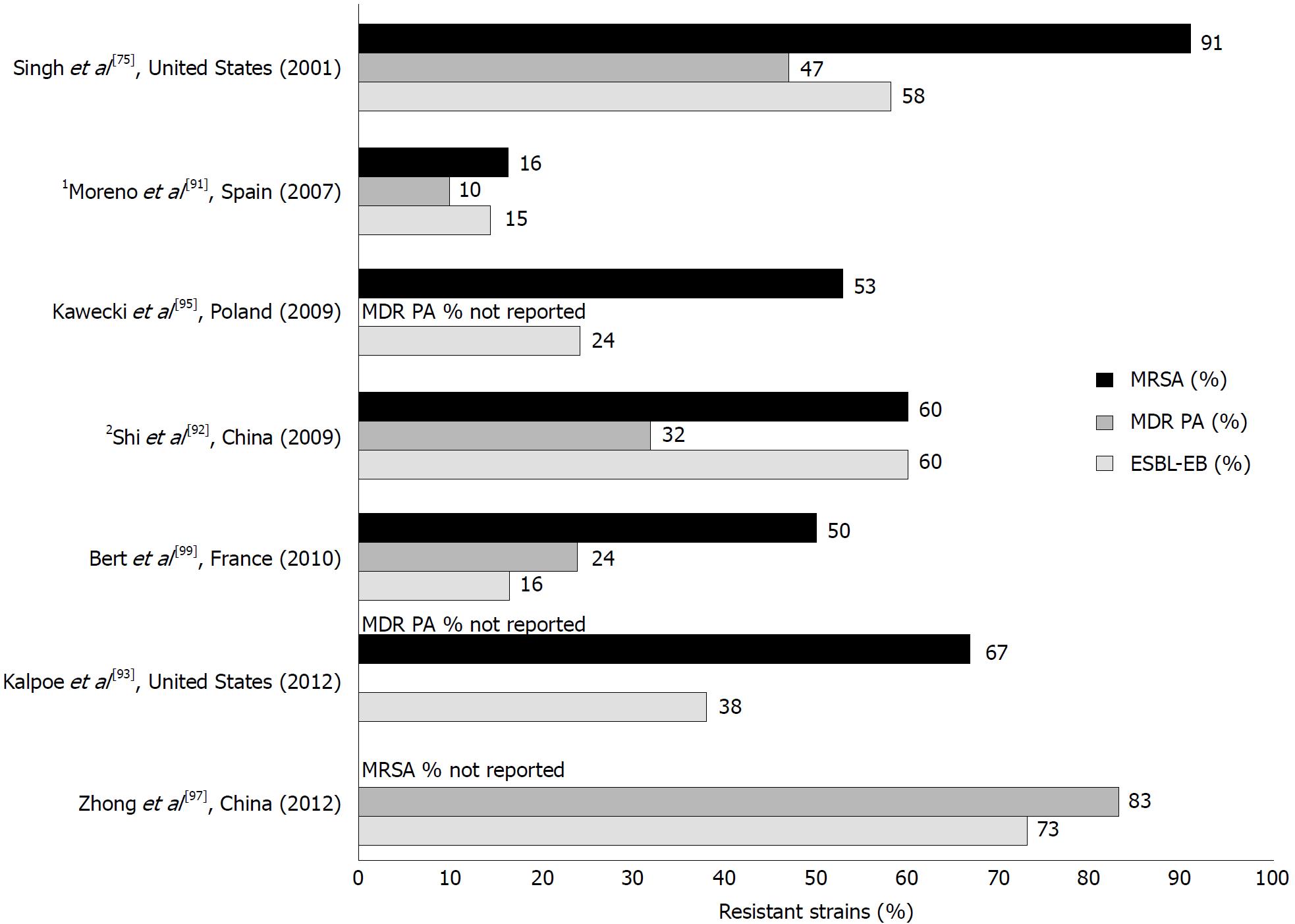
Figure 2 Studies reporting the percentage of infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae following liver transplantation[79,91-93,95-97].
1Data reported for all solid organ transplants; 2MRSA data obtained from reference 98[98]. MRSA: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MDR-PA: Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa; ESBL-EB: Extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase Enterobacteriaceae.
- Citation: Righi E. Management of bacterial and fungal infections in end stage liver disease and liver transplantation: Current options and future directions. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(38): 4311-4329
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i38/4311.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i38.4311