Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2018; 24(15): 1601-1615
Published online Apr 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i15.1601
Published online Apr 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i15.1601
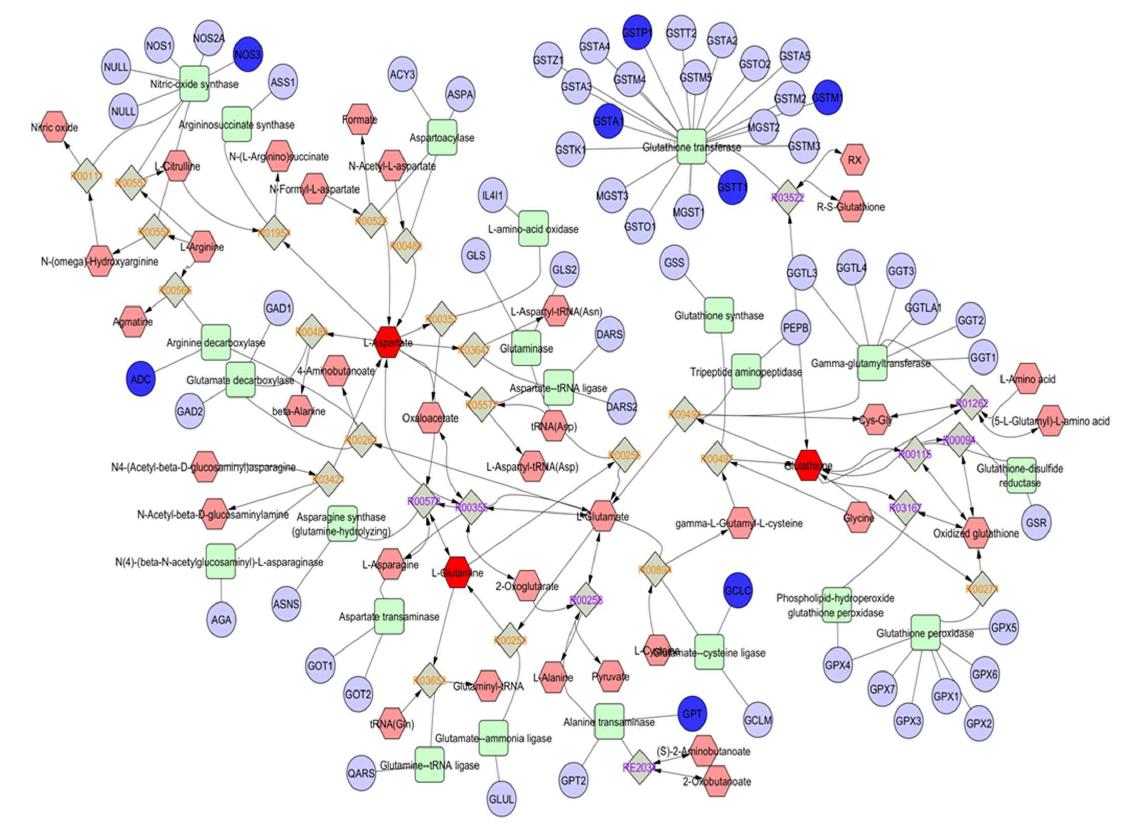
Figure 4 The urea-cycle, glutamate, and branched-chain amino acids in the biology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Sub-network analysis showing the urea-cycle and metabolism of amino acids (L-arginine, L-proline, L-glutamate, L-aspartate and L-asparagine) that were extracted from the interactome shown in Figure 3. Compounds (common names in the Human Metabolome Database, http://www.hmdb.ca), chemical reactions, enzymes (KEGG database) and genes (HUGO symbols) are represented by hexagons, diamonds, squares and circles, respectively.
- Citation: Pirola CJ, Sookoian S. Multiomics biomarkers for the prediction of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease severity. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(15): 1601-1615
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i15/1601.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i15.1601