Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2016; 22(41): 9127-9140
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9127
Published online Nov 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9127
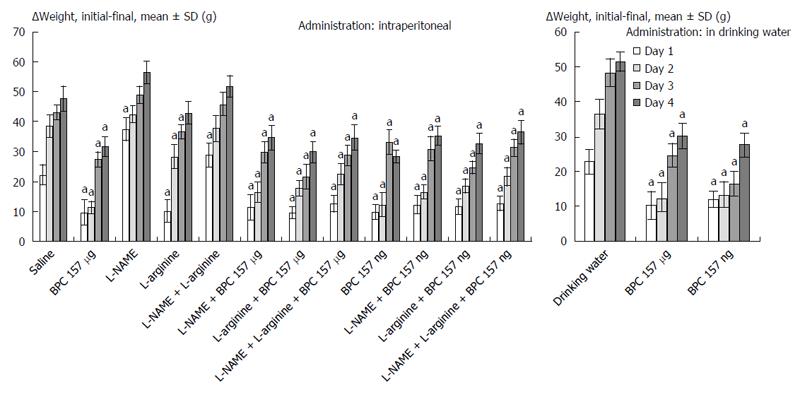
Figure 5 Weight loss (g) presented as the Δ between the initial and final weights[13,18], mean ± SD, in rats that underwent esophagogastric anastomosis.
Medication (/kg) given intraperitoneally (once time daily) or continuously in drinking water after the creation of an esophagogastric anastomosis in rats. BPC 157 10 μg and 10 ng, L-NAME 5 mg, and L-arginine 100 mg given alone and/or combined intraperitoneally with the first application at 30 min after anastomosis creation and the last at 24 h before sacrifice. Drinking water alone (12 mL/d per rat) or BPC 157 in drinking water (10 μg and 10 ng/kg; 0.16 μg and 0.16 ng/mL) was provided continuously until sacrifice. aP < 0.05, at least, vs control.
- Citation: Djakovic Z, Djakovic I, Cesarec V, Madzarac G, Becejac T, Zukanovic G, Drmic D, Batelja L, Zenko Sever A, Kolenc D, Pajtak A, Knez N, Japjec M, Luetic K, Stancic-Rokotov D, Seiwerth S, Sikiric P. Esophagogastric anastomosis in rats: Improved healing by BPC 157 and L-arginine, aggravated by L-NAME. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(41): 9127-9140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i41/9127.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i41.9127