Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2016; 22(1): 435-445
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.435
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.435
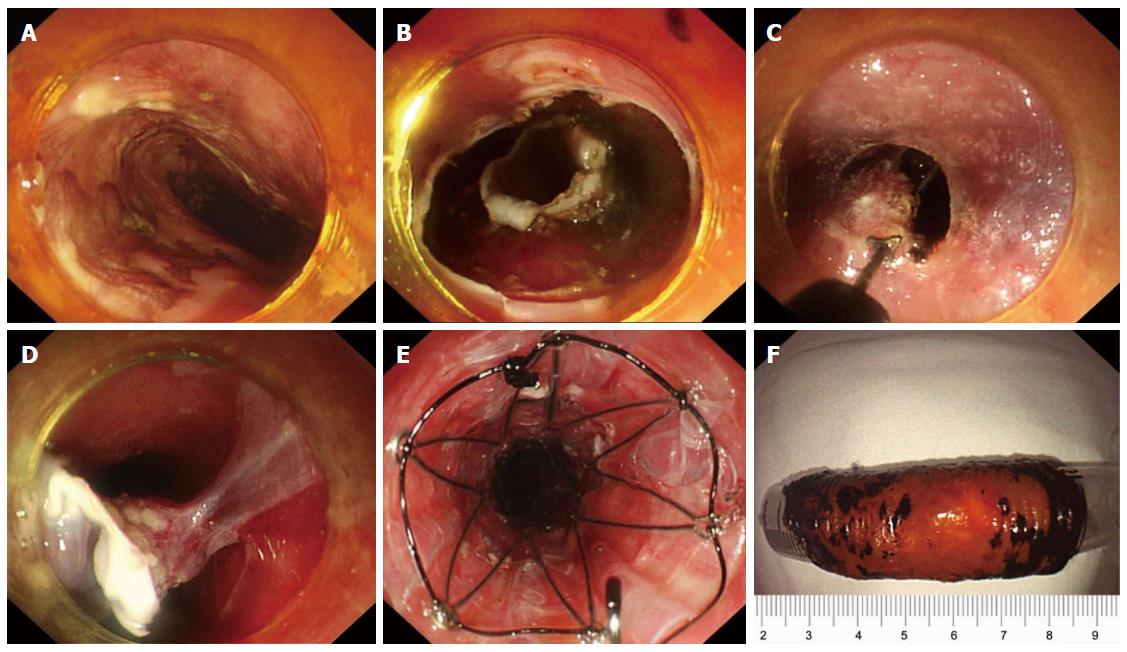
Figure 4 Double-tunnel endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for circumferential superficial esophageal neoplasms.
A: An 8 cm circumferential superficial esophageal cancer was showed by iodine staining, at 28–36 cm from the incisors; B: Circular incisions were successively performed at the anal and oral margins after marking; C, D: Two submucosal tunnels were created opposite each other. Two tunnels nearly covered the whole esophageal lumen, and the borders were narrow enough to be resected easily; E: A 14 cm retrievable, fully-covered esophageal stent was placed to prevent postoperative stenosis. F: The lesion was resected circumferentially, about 60 mm in length. From Zhai et al[20].
- Citation: Zhai YQ, Li HK, Linghu EQ. Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for large superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(1): 435-445
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i1/435.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.435