Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2016; 22(1): 349-360
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.349
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.349
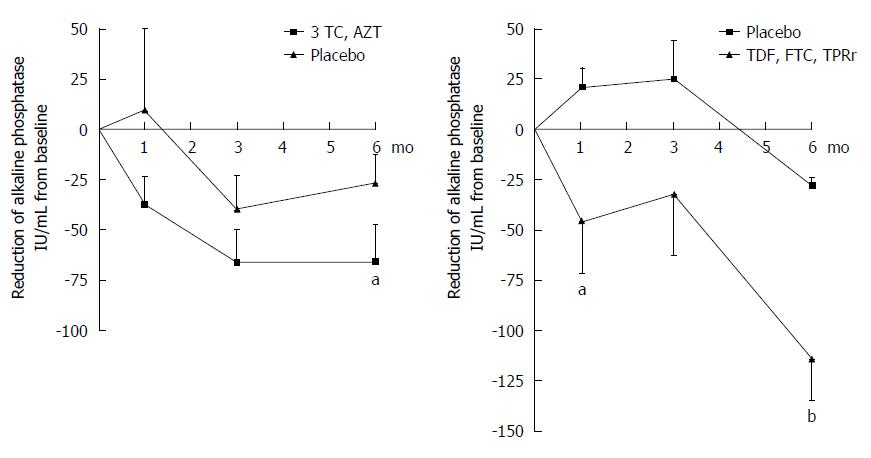
Figure 5 Incremental improvement of hepatic biochemistry observed in primary biliary cirrhosis patients maintained on UDCA receiving combination antiretroviral therapy with a protease inhibitor.
Patients treated with daily lamivudine 150 mg (3TC) and zidovudine 300 mg (AZT) developed a 66 IU/mL mean reduction in ALP, whereas those receiving daily tenofovir/emtricitabine 300/200 mg (TDF, FTC) and lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg (LPRr) for 6 mo (n = 13) experienced a mean ALP reduction of 114 IU/mL (two-way ANOVA, bP < 0.001, aP < 0.05 vs control). With permission, adapted from Mason et al[11].
- Citation: Lytvyak E, Montano-Loza AJ, Mason AL. Combination antiretroviral studies for patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(1): 349-360
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i1/349.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.349