Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2016; 22(1): 349-360
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.349
Published online Jan 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.349
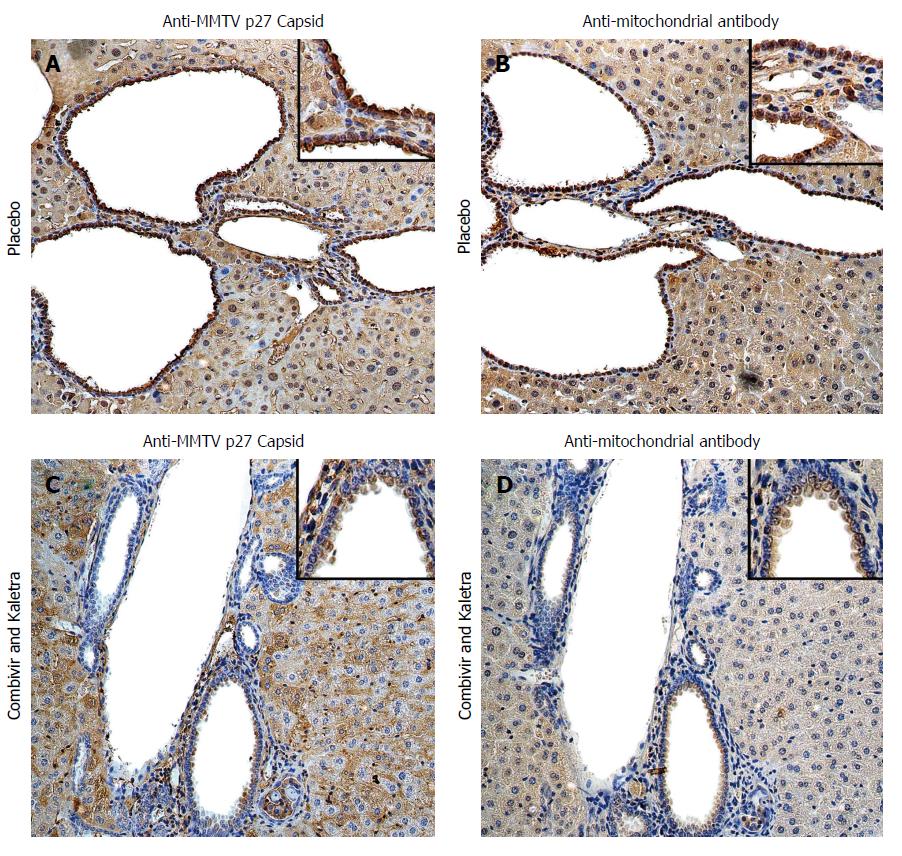
Figure 1 Hepatic immunohistochemistry study of NOD.
c3c4 mice treated with placebo (A and B) or tenofovir/emtricitabine and lopinavir/ritonavir (C and D) for 12 wk. A: Mice receiving placebo showed anti-MMTV p27 Capsid reactivity in biliary epithelial cells and hepatocyte nuclei to a lesser extent; B: The distribution of anti-mitochondrial antibody staining was observed in a similar biliary distribution pattern on the bile duct epithelium; C and D: The reactivity to both viral and mitochondrial proteins was attenuated in mice treated with tenofovir/emtricitabine and lopinavir/ritonavir. Haematoxylin eosin staining, magnification × 2009 with × 4009 in insets showing staining in biliary epithelial cells. With permission from Sharon et al[8].
- Citation: Lytvyak E, Montano-Loza AJ, Mason AL. Combination antiretroviral studies for patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(1): 349-360
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i1/349.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.349