Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2015; 21(38): 10739-10748
Published online Oct 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10739
Published online Oct 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10739
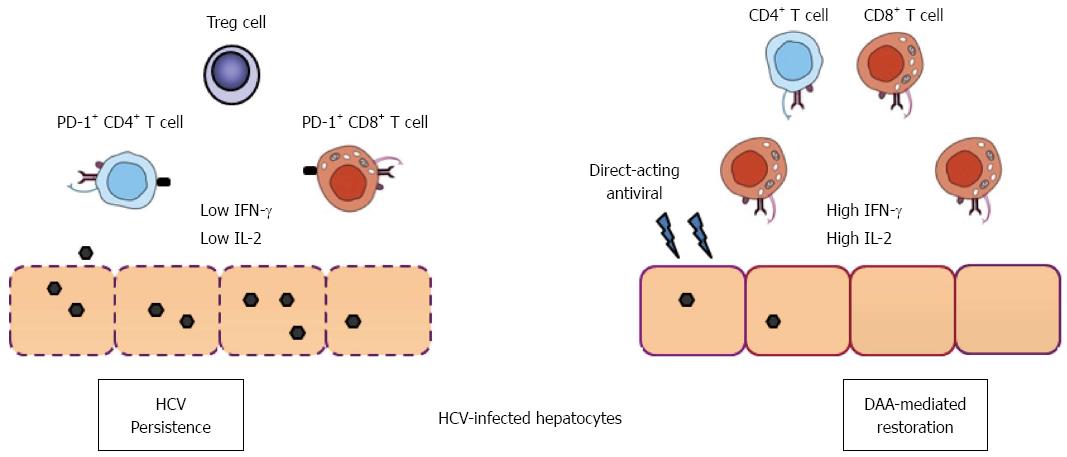
Figure 1 Direct-acting antiviral therapy and immune function restoration in hepatitis C virus infection.
In chronic hepatitis C infection, T cells having a narrow repertoire of TCRs mount a weak response to HCV antigens, and their effector functions are often impaired. Many CD8+ and CD4+ T cells express low levels of IFN-γ and IL-2 accompanied by up-regulation of PD-1 molecules in the liver. Development of T regulatory cells and compromised dendritic cell functions also contribute to T cell functional impairment. Recent data suggest that IFN-free direct-acting antivirals not only clear HCV in the majority of patients, but also result in the down-regulation of PD-1, leading to rapid restoration of virus-specific CD8+ T cell functions in patients[28]. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; PD-1: Program death-1; TCR: T cell receptor.
- Citation: Sun J, Rajsbaum R, Yi M. Immune and non-immune responses to hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(38): 10739-10748
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i38/10739.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10739