Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2015; 21(3): 711-725
Published online Jan 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.711
Published online Jan 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.711
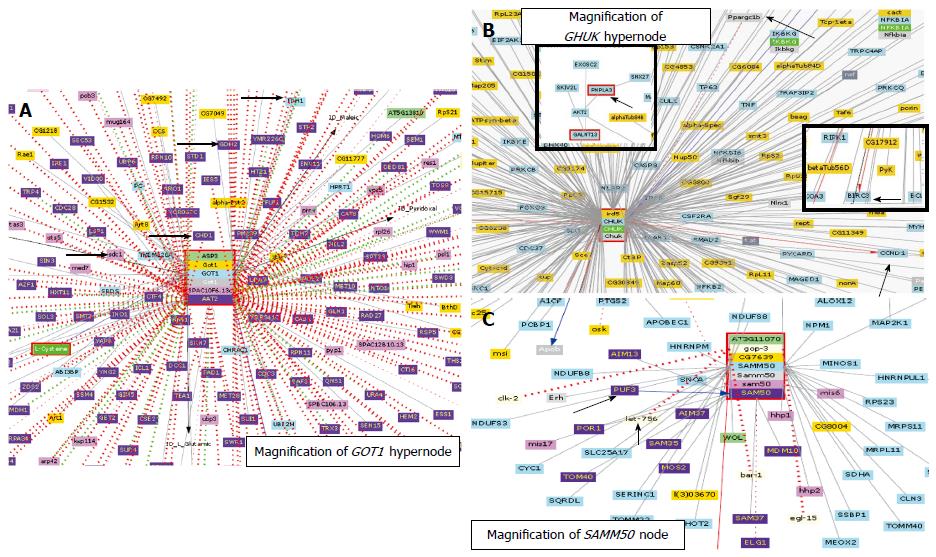
Figure 3 Biomolecular interactions focused on hypernodes (GOT1 and CHUK) and nodes (SAMM50) predicted by the visualization tool for systems biology Cognoscente.
Cognoscente currently contains over 413000 documented interactions, with coverage across multiple species, including Homo sapiens, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Drosophila melanogaster, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Arabidopsis thaliana, Mus musculus, and Caenorhabditis elegans, among others[74]. Colors under the hypernode/node gene name denote different species; for example, light blue corresponds to homo sapiens, blue to saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c and violet to schizosaccharomyces pombe; light green is arabidopsis thaliana, orange is Drosophila melanogaster, red is Gallus gallus, gray is rattus norvegicus and pale gray is caenorhabditis elegans. Arrows highlight biomolecular interactions discussed in the body of the manuscript.
- Citation: Sookoian S, Pirola CJ. Liver enzymes, metabolomics and genome-wide association studies: From systems biology to the personalized medicine. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(3): 711-725
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i3/711.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.711