Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2014; 20(6): 1529-1536
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1529
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1529
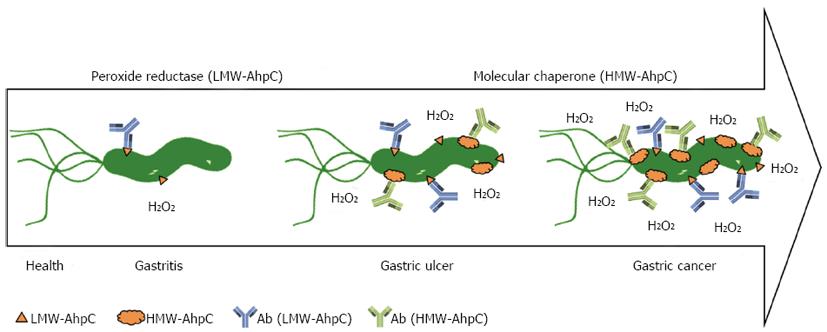
Figure 4 Alkylhydroperoxide reductase of Helicobacter pylori, a biomarker used to monitor different stages of inflammation associated with gastrointestinal diseases.
In cases of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, none or low titers of serum antibody against low-molecular-weight (LMW)-alkylhydroperoxide reductase (AhpC) were detected in patients of gastritis with weak inflammation. However, higher titers of antibodies against high-molecular-weight (HMW)-AhpC were found in gastric ulcer and cancer patients with severe inflammation. Therefore, H. pylori AhpC can signal and monitor different stages of inflammation associated with H. pylori infection in gastrointestinal diseases[37].
-
Citation: Huang CH, Chiou SH. Clinical proteomics identifies potential biomarkers in
Helicobacter pylori for gastrointestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(6): 1529-1536 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i6/1529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1529