Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2014; 20(47): 17804-17818
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17804
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17804
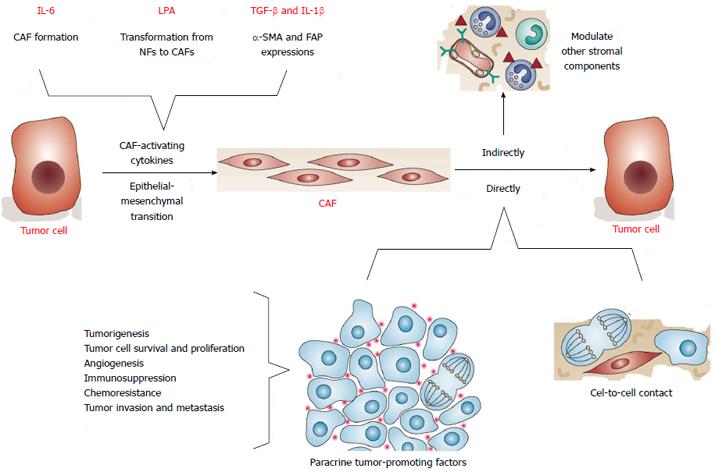
Figure 2 The interplay between cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells.
Tumor cells activate CAFs by secreting various cytokines and epithelial-mesenchymal transition; CAFs exert their tumor-promoting function through direct (paracrine soluble factors and cell-to-cell contact) and indirect (modulating other stromal components) approaches (Elements adapted from Mueller et al[110]). CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblast; LPA: Lysophostatidic acid; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; NF: Normal fibroblast; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Huang L, Xu AM, Liu S, Liu W, Li TJ. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in digestive tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(47): 17804-17818
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i47/17804.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17804