Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2014; 20(31): 10876-10885
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10876
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10876
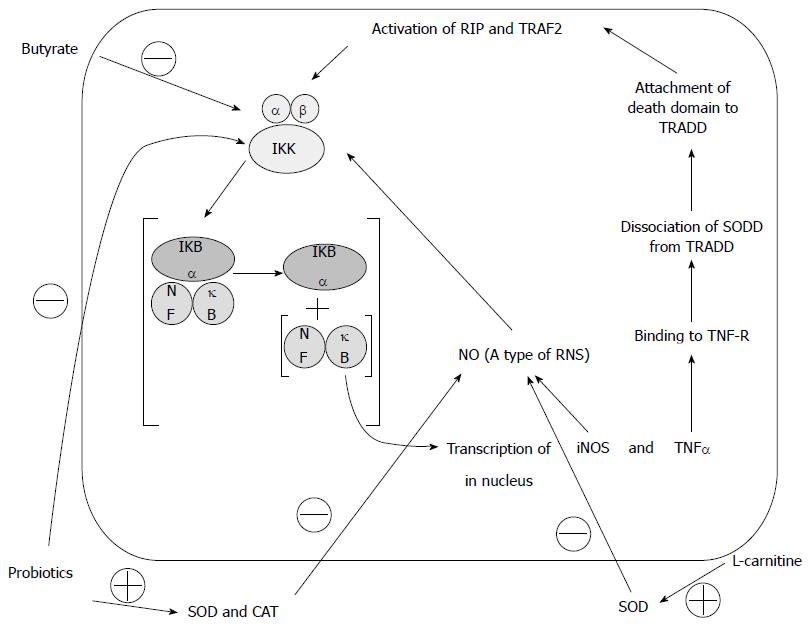
Figure 7 Effects of butyrate, L-carnitine, and probiotics on Ikappa B kinase.
Adopted from authors’s previous Open Access publication (Moeinian et al. Synergistic effect of probiotics, butyrate and L-carnitine in treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). J Med Hypotheses Idea 2013; 7: 50-53)[11]. SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; IKK: IκB kinase; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; NO: Nitric oxide; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; RIP: Ribosome inactivating protein; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNF-R: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; TRADD: Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated death domain protein; TRAF2: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 2; SODD: Silencer of death domain.
-
Citation: Moeinian M, Ghasemi-Niri SF, Mozaffari S, Abdolghaffari AH, Baeeri M, Navaea-Nigjeh M, Abdollahi M. Beneficial effect of butyrate,
Lactobacillus casei and L-carnitine combination in preference to each in experimental colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(31): 10876-10885 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i31/10876.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10876