Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 9775-9827
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9775
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9775
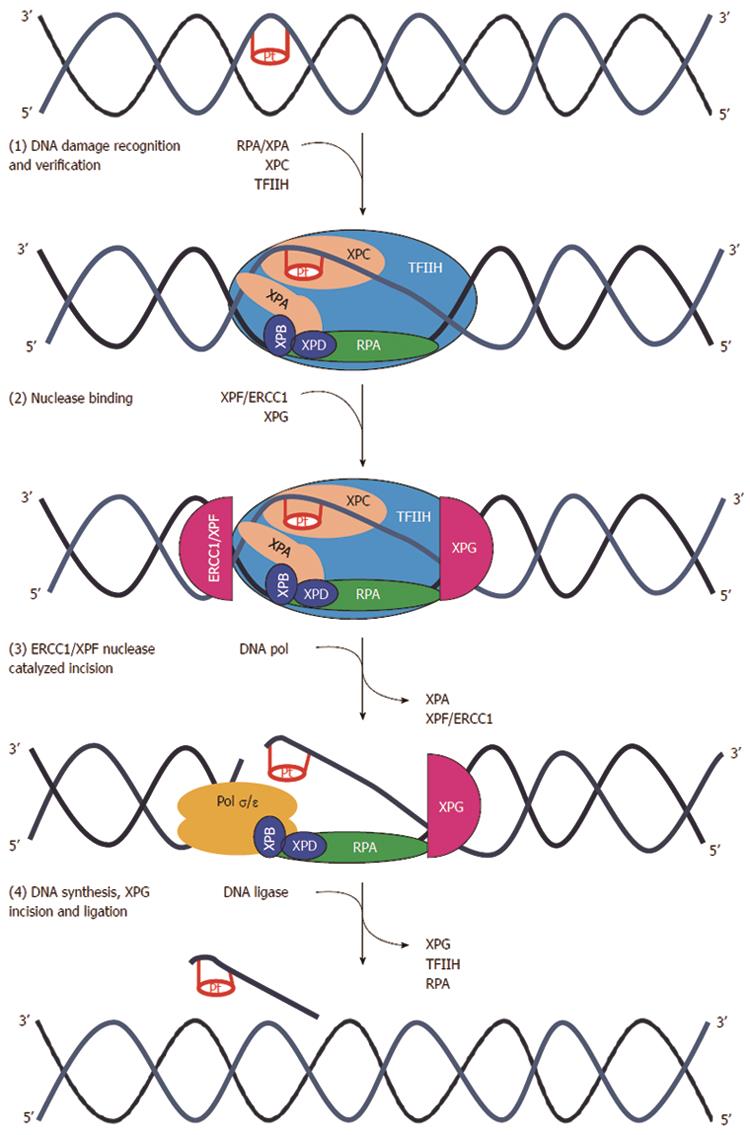
Figure 9 Nucleotide excision repair pathway.
(1) DNA damage formed by platinum agents leads to DNA double helix distortion. Several distinct complexes are involved in sequential steps than can be summarized as DNA damage recognition (XPCHR23B), damage demarcation, and verification (TFIIH), assembly of a preincision complex (RPA and XPA) and helix unwinding (XPB and XPD); (2) Endonuclease recruitment with dual incision of the damaged strand on the 5’ side (ERCC1-XPF heterodimers) and 3’ side (XPG) followed by the removal of the excised oligomer; (3) DNA repair synthesis to fill in the resulting gap; and (4) ligation. ERCC1: Excision repair cross-complementation group 1; Pol σ/ε : Polymerase σ/ε; RFC: Replication factor C; TFIIH: Transcription factor II H; XP (A,B,C,D,F,G): Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group (A,B,C,D,F,G)[340].
- Citation: Panczyk M. Pharmacogenetics research on chemotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer over the last 20 years. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 9775-9827
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/9775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9775