Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 9775-9827
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9775
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9775
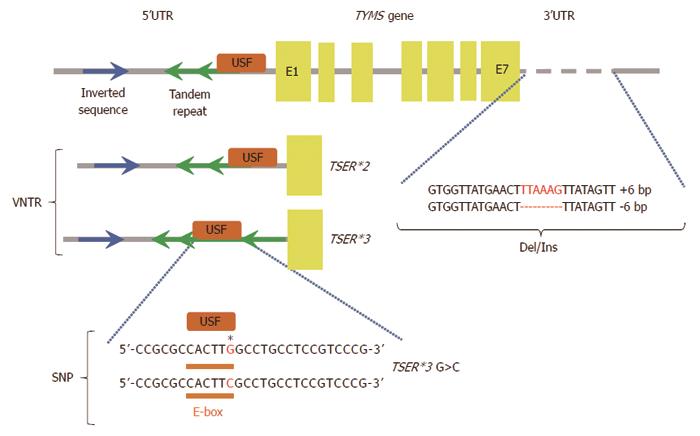
Figure 3 Some of the described polymorphisms affect inter-individual differences in patient sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil treatment.
Polymorphisms in the thymidylate synthase gene (TYMS gene), 5’ and 3’ untranslated regions (5’UTR and 3’UTR), exons (E1-E7), binding site for upstream stimulating factor (USF), variable number tandem repeats (VNTR), single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), deletion/insertion polymorphism (Del/Ins), two-tandem repeats (TSER*2), three-tandem repeats (TSER*3), TSER*3 G>C (single nucleotide polymorphism of TSER*3). Regulation of TYMS gene expression. TSER polymorphism (TS 2R/3R repeat) is a tandem repeat upstream of the TYMS translational start site containing either double (2R) or triple (3R) repeats of 28-bp sequences. These tandem repeats regulate transcription and translation of TYMS. Additional functional variants of the TYMS gene have been identified and TSER 2R/3R repeat is now studied together with a G to C SNP within the second repeat of the 3R allele. TSER 3RC/3RC genotype causes lower transcriptional activity of TYMS, comparable with the TS 2R/2R genotype. TS 1494del6bp is another functional variant of the TYMS gene and has been shown to decrease RNA stability and therefore influence TS mRNA and TS protein expression in vitro[52].
- Citation: Panczyk M. Pharmacogenetics research on chemotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer over the last 20 years. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 9775-9827
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/9775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9775