Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 9716-9731
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9716
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9716
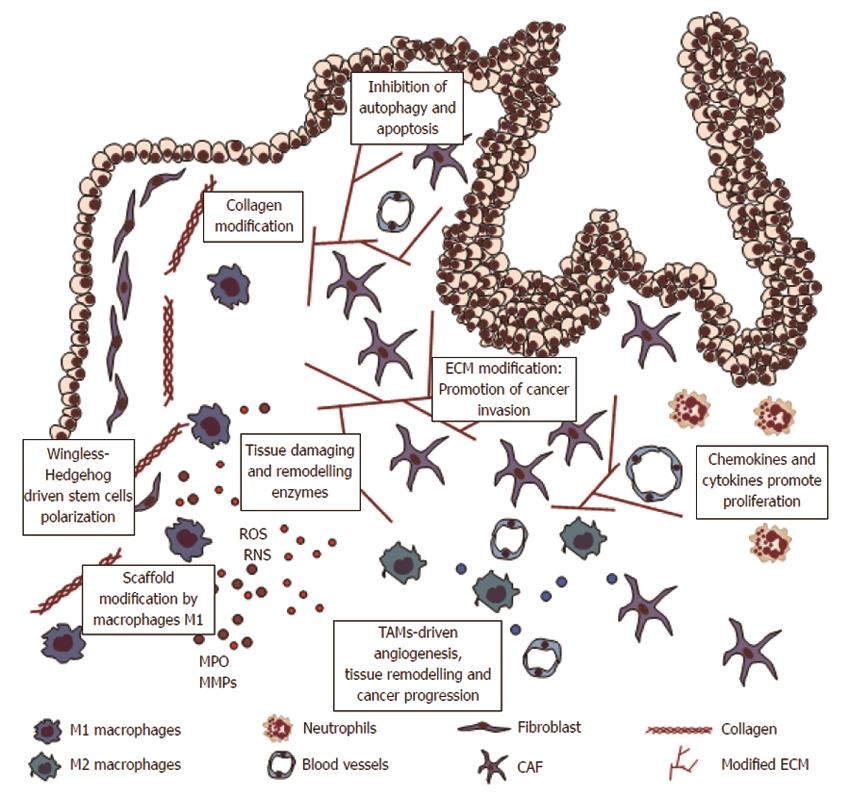
Figure 3 Inflammation and remodelling of colorectal mucosa.
Macrophages and neutrophils cause tissue damage and DNA damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation. Inflammatory cytokines stimulate crypt stem cells proliferation driven by Wingless and Hedgehog. Defects in apoptosis and autophagy systems cause accumulation and proliferation of transformed cells. Indeed, inflammatory cells cause extracellular matrix (ECM) modifications, substaining disassembly of normal tissue architecture, angiogenesis and tumor invasion. CAF: Carcinoma associated fibroblasts; TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinases.
- Citation: Mariani F, Sena P, Roncucci L. Inflammatory pathways in the early steps of colorectal cancer development. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 9716-9731
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/9716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9716