Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2014; 20(27): 8751-8763
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751
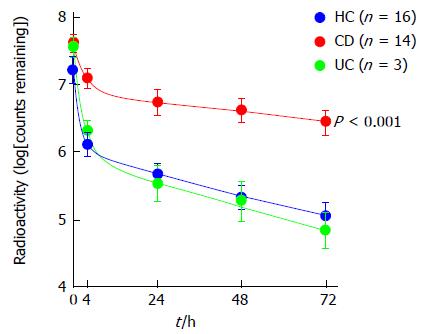
Figure 2 Patients with Crohn’s disease exhibit reduced bacterial clearance of subcutaneously injected 32P-labelled heat-killed Escherichia coli relative to healthy controls and patients with ulcerative colitis.
Reproduced with permission. © 2009 Rockefeller University Press. Originally published in Journal of Experimental Medicine 206: 1883-1897[45]. CD: Crohn’s disease; HC: Healthy controls; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
-
Citation: Tawfik A, Flanagan PK, Campbell BJ.
Escherichia coli -host macrophage interactions in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(27): 8751-8763 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i27/8751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751