Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2014; 20(21): 6400-6411
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6400
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6400
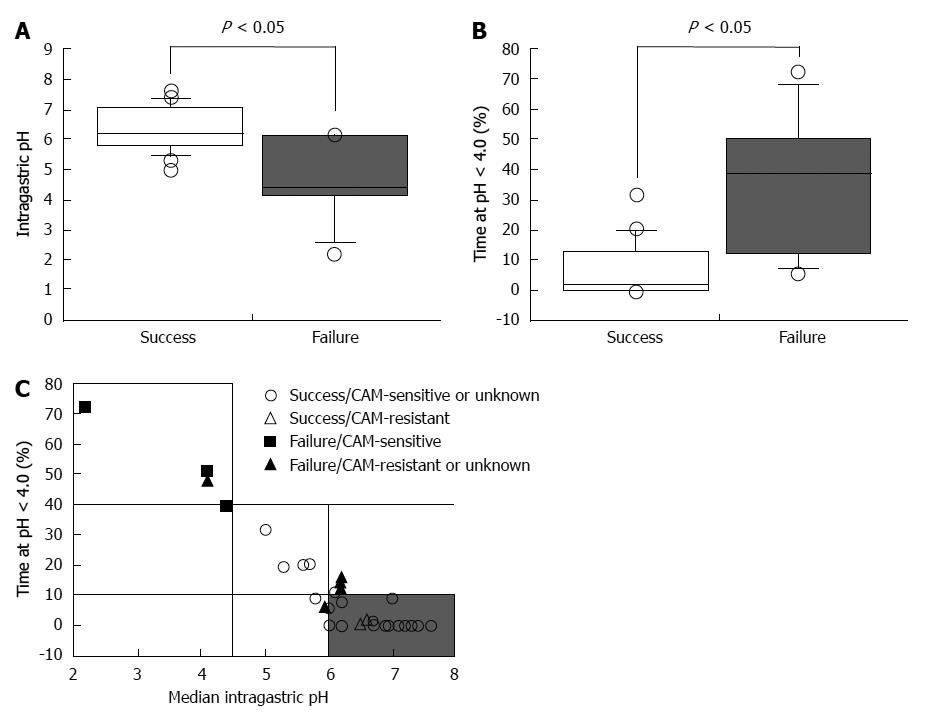
Figure 1 Success of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment as a function of pH.
A, B: Median 24-h pH values (A) and the percentage of the times when pH < 4.0 during eradication therapy according to successful and failed treatment (B); C: Variation of pH and the percentage of time at pH < 4.0[51]. The median pH of successfully treated patients was significantly higher than compared with patients that failed treatment (A). The median percentage of the time when pH < 4.0 in successfully treated patients was significantly shorter compared with unsuccessfully treated patients (B). The majority of patients were cured using triple therapy when the percentage of time at pH < 4.0 during the 24-h post-dose period was < 10% and the 24-h pH was > 6.0 (shaded area) (C). CAM: Clarithromycin.
-
Citation: Sugimoto M, Furuta T. Efficacy of tailored
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy based on antibiotic susceptibility andCYP2C19 genotype. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(21): 6400-6411 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i21/6400.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6400