Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4467-4482
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4467
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4467
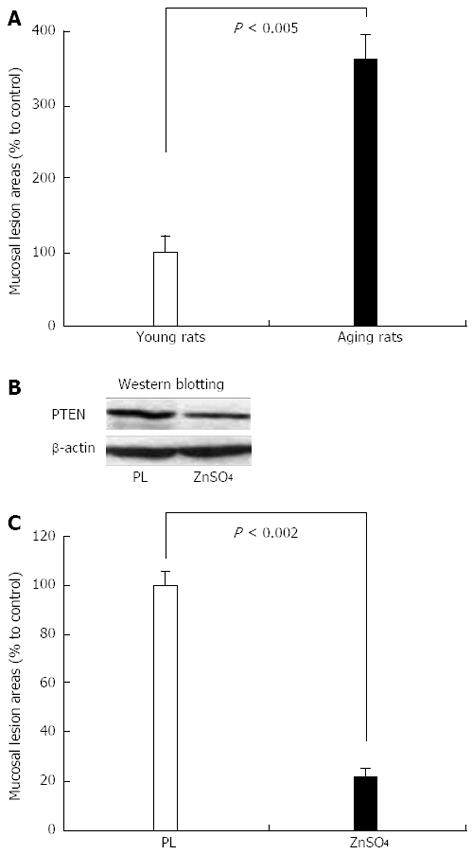
Figure 11 Extent of ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in young and aging rats.
A: Three hours after intragastric administration of 8 mL/kg of 50% ethanol, gastric mucosal injury is significantly increased in aging rats vs young rats; B: Intragastric administration of ZnSO4 for 4 h (2 mL 0.5% solution) downregulates phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) protein expression in gastric mucosa of aging rats vs placebo control (PL); C: Intragastric administration of ZnSO4 to aging rats for 4 h completely reverses the increased susceptibility of gastric mucosa to ethanol-induced injury indicating a causal relationship between PTEN and mucosal injury. Reproduced with permission from Tarnawski et al[1].
- Citation: Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A, Jones MK. Increased susceptibility of aging gastric mucosa to injury: The mechanisms and clinical implications. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4467-4482
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4467.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4467