Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4467-4482
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4467
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4467
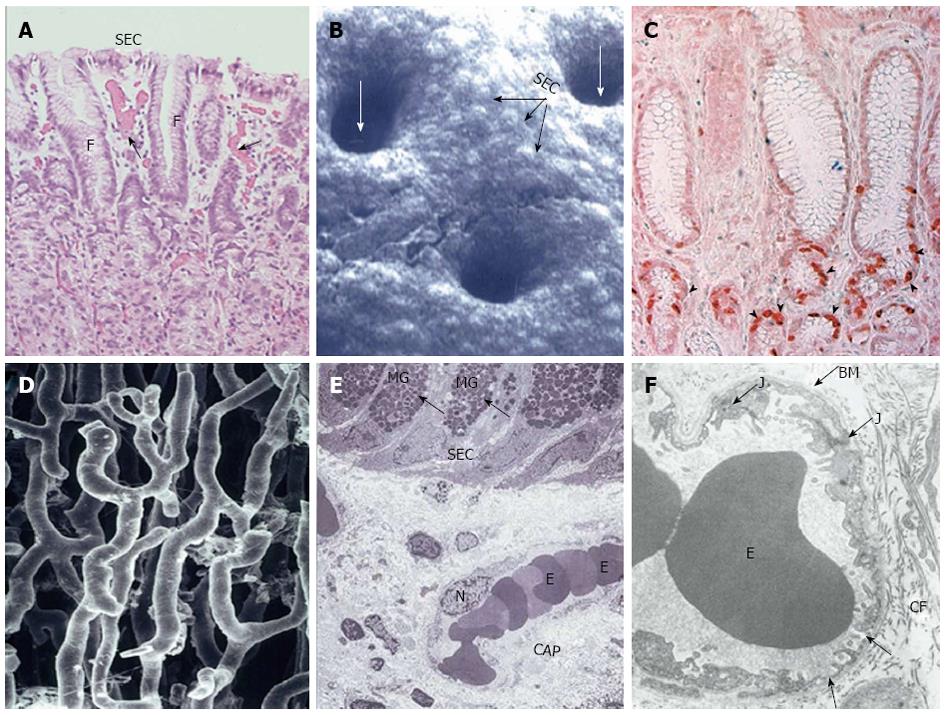
Figure 3 Structural components of gastric mucosal defense: surface epithelial cells, progenitor cells and blood microvessels.
Reproduced with permission from Laine, Takeuchi and Tarnawski[4]. A: Histology of upper part of human gastric mucosa visualizing surface epithelial cells (SEC), foveoli (F), and upper gland area. (Hand E staining; original magnification, × 50). Blood microvessels with erythrocytes in the lumen are present in the lamina propria (arrows); B: Scanning electromicrograph of human gastric mucosal luminal surface. The unstirred mucus gel layer is not seen because of dissolution during fixation. Individual SEC are clearly visible as are lumina of the gastric pits (white arrows). Reproduced with permission from Tarnawski et al[7]; C: Immunostaining of human gastric mucosa with survivin (anti-apoptosis protein) antibody. Survivin is strongly expressed (brown-red staining) in the epithelial progenitor cells located in the foveolar/neck area (arrowheads). Reproduced with permission from Tarnawski et al[1]; D: Vascular cast study of capillary blood vessels in the gastric mucosa using Mercox resin. The remaining components of the mucosa were dissolved with concentrated NaOH. Reproduced with permission from Ichikawa, Tarnawski et al[8]; E: Transmission electron micrograph of normal human gastric mucosa. SEC contain dark mucus granules (MG, arrows). Below the surface epithelial cells, a capillary blood vessel (CAP) with erythrocytes (E) in the lumen is present in the lamina propria. N, nucleus of endothelial cell lining capillary vessel (original magnification, × 2000). Reproduced with permission from Tarnawski et al[9]; F: Transmission electron micrograph of a portion of human gastric capillary blood vessel. The structure of the capillary wall and endothelial cell cytoplasm is normal with a characteristic fenestration (arrows) allowing transport. BM: Basement membrane; E: Erythrocytes in the capillary lumen; J: Junction between two neighboring endothelial cells; CF: Collagen fibers. Original magnification, × 17400. Reproduced with permission from Tarnawski et al[9].
- Citation: Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A, Jones MK. Increased susceptibility of aging gastric mucosa to injury: The mechanisms and clinical implications. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4467-4482
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4467.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4467