Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2013; 19(12): 1890-1900
Published online Mar 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.1890
Published online Mar 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.1890
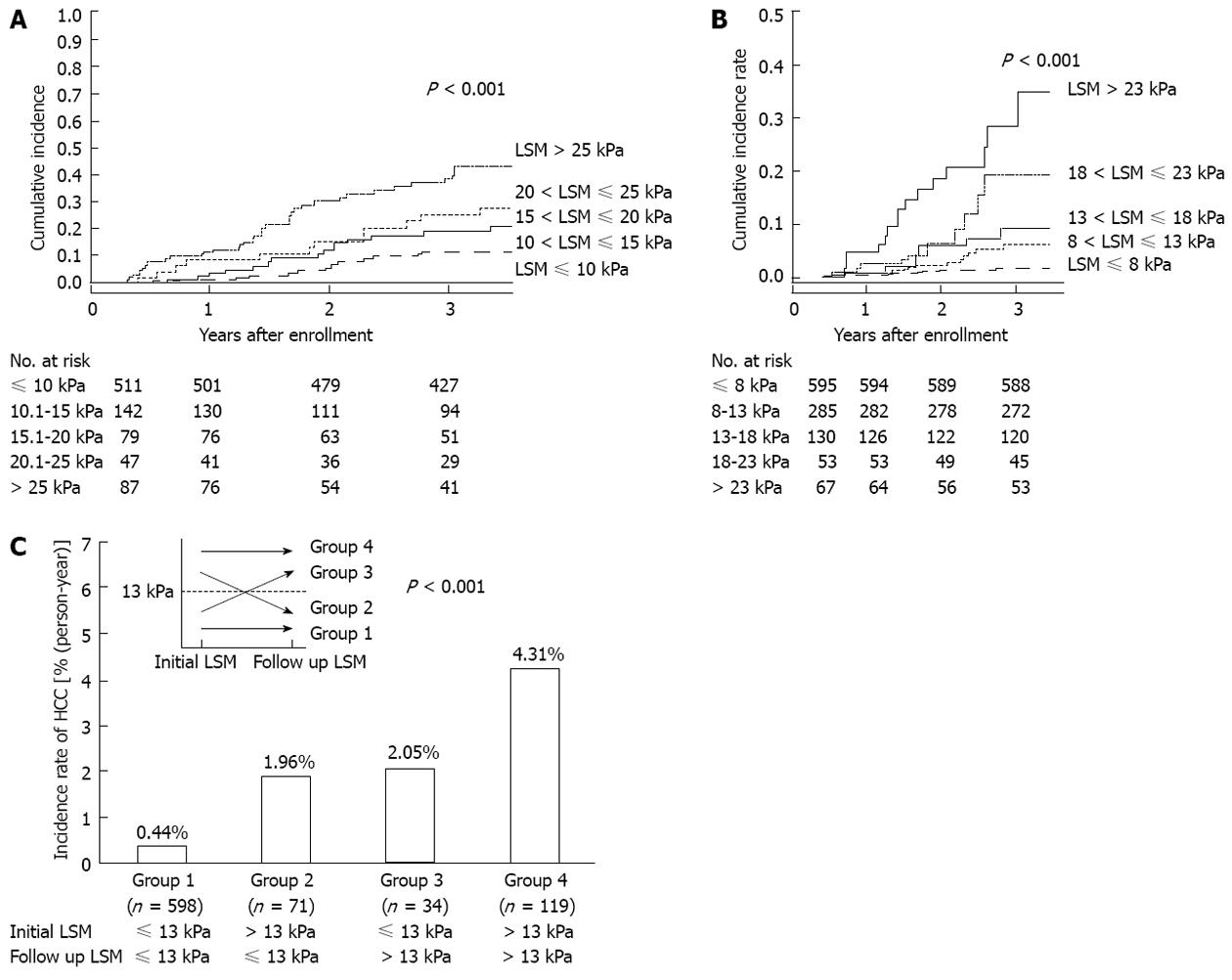
Figure 2 Cumulative incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma development based on stratified transient elastography values in patients with chronic hepatitis C (A, n = 866) and those with chronic hepatitis B (B, n = 1130).
The cumulative incidences increased significantly in association with higher TE values (log-rank test, all P < 0.001). In particular, the overall incidence of HCC differed significantly among the four groups (C) (both initial and follow-up TE values ≤ 13 kPa (group 1), initial TE value > 13 kPa and follow-up TE value ≤ 13 kPa (group 2), initial TE value ≤ 13 kPa and follow-up TE value > 13 kPa (group 3), and both initial and follow-up TE values > 13 kPa (group 4) according to changing patterns of TE value during follow-up (P < 0.001; Figure 2C). A: Cited from Masuzaki et al[52]; B and C: Cited from Jung et al[53]. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; TE: Transient elastography; LSM: Liver stiffness measurement.
- Citation: Kim BK, Fung J, Yuen MF, Kim SU. Clinical application of liver stiffness measurement using transient elastography in chronic liver disease from longitudinal perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(12): 1890-1900
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i12/1890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.1890