Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2012; 18(5): 425-434
Published online Feb 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.425
Published online Feb 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.425
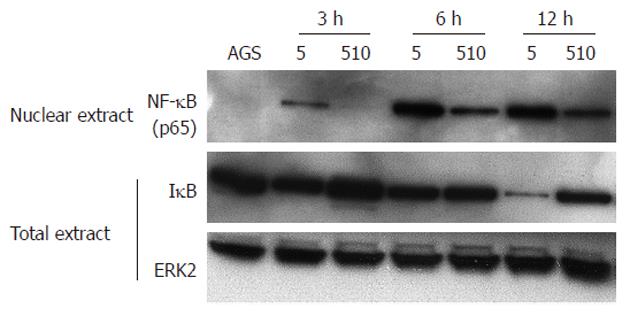
Figure 4 Detection of nuclear factor kappa B (p65) (upper), inhibition kappa B (middle) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (bottom) in nuclear and total extracts, respectively at 3, 6 and 12 h after being co-cultured with Helicobacter pylori.
Unphosphorylated extracellular signal–regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) was detected as the control in this study[23]. Molecular weights of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), inhibition kappa B (IκB) and ERK2 are 65, 35-37 and 42 kDa, respectively. The assay was carried out with strains at a MOI of 150. AGS: AGS cells co-cultured without H. pylori; HPK5: AGS cells co-cultured with wild-type HPK5; HPKT510: AGS cells co-cultured with cdrA-disrupted mutant HPKT510.
-
Citation: Takeuchi H, Zhang YN, Israel DA, Peek Jr RM, Kamioka M, Yanai H, Morimoto N, Sugiura T. Effect of
Helicobacter pylori cdrA on interleukin-8 secretions and nuclear factor kappa B activation. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(5): 425-434 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i5/425.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.425