Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2009; 15(29): 3611-3620
Published online Aug 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3611
Published online Aug 7, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3611
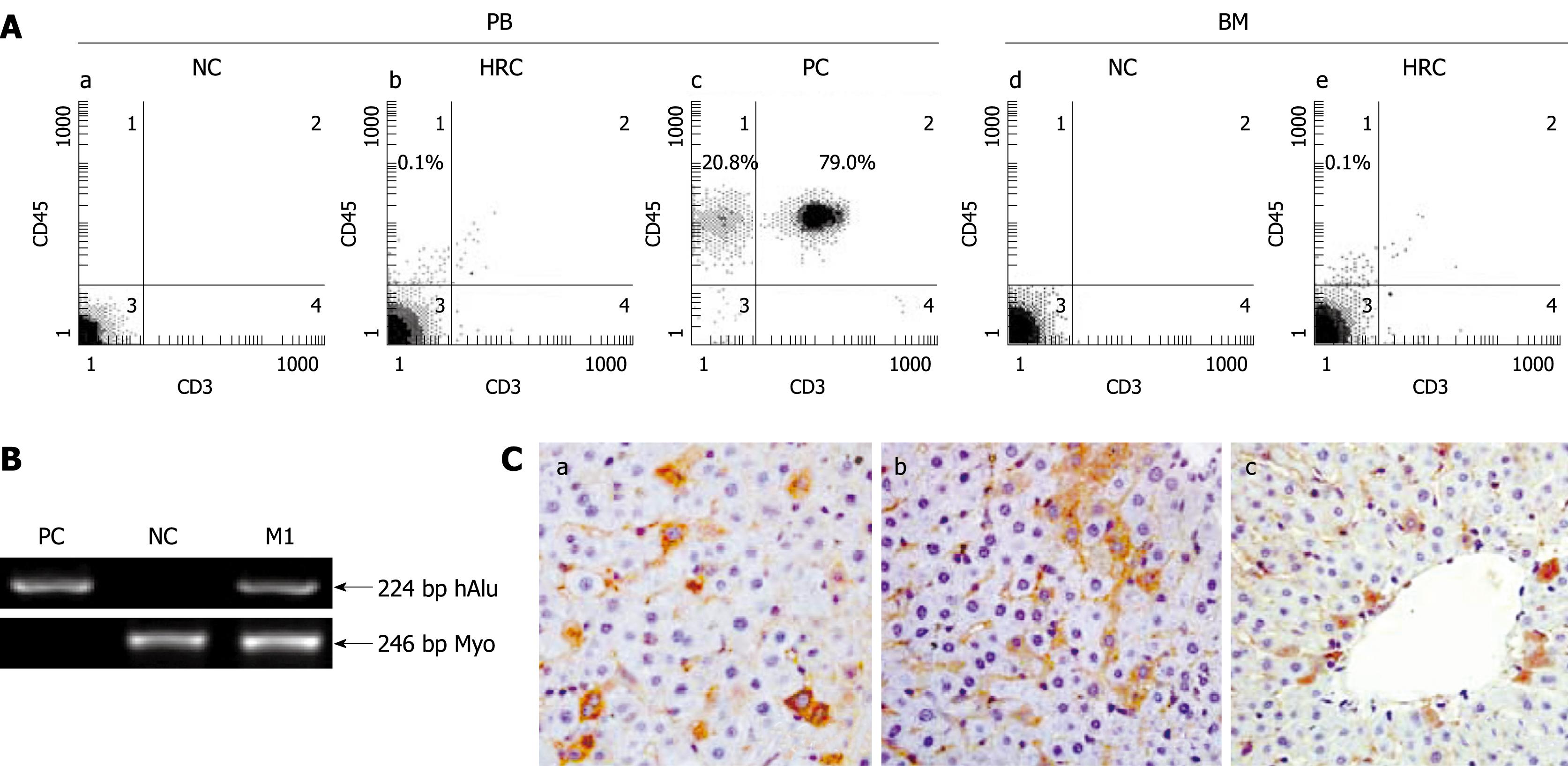
Figure 1 Screening for human-rat chimera (HRC) derived from in utero transplantation of hUCB-MNCs.
Human-rat hybrid animals were produced by in utero transplantation of low-density mononuclear cells (MNCs) from human umbilical cord blood (hUCB) into fetal rats at the gestation of 9-11 d. A: Representative flow cytometric analysis of human CD45-positive cell engraftment in PB and BM of HRC. After birth, peripheral blood (PB) was collected at the indicated time points. The collected blood cells were stained with anti-human CD45 and CD3 antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. MNC-transplanted rat (MTR) was killed at end of each experiment, with bone morrow (BM) obtained and assessed for human CD45+ cell engraftment by 2-color flow cytometry. Human PB from healthy volunteers was used as a positive control (PC) and normal rat PB was used a negative control (NC); B: Identification of human genes in liver of MTR by human gene-specific PCR. To determine the human donor contribution in the liver of MTR, PCR was carried out on genomic DNA with primers specific for hAlu gene[19]. The PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis from positive-control human blood genomic DNA (lane PC), normal/non-transplanted rat genomic DNA (lane NC) and genomic DNA prepared from liver of one MTR was shown. Rat myogenin (Myo)-specific PCR was carried out for quality and quantity controls of genomic DNA with primers specific for rat Myo gene[19]. Data are representative of three independent PCRs yielding similar results. Arrow indicates the position of PCR products amplified by the primers for hAlu[19]. M1: Molecular weight DNA marker (DL2000, TaKaRa); C: Immunohistochemical analysis of various human antigens in liver of MTR. In the receipt liver, donor-derived human cells with different cellular phenotypes were detected by IHC for different human markers, such as β2-microglobulin [β2-M (a), CK18 (b) and CK19 (c)]. Brown staining shows positive human cells in various tissues from MTR and human samples (data not shown), whereas no positive human cells were found in normal control (NC) rats (data not shown).
- Citation: Sun Y, Xiao D, Li HA, Jiang JF, Li Q, Zhang RS, Chen XG. Phenotypic changes of human cells in human-rat liver during partial hepatectomy-induced regeneration. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(29): 3611-3620
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i29/3611.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.3611