Copyright
©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2009; 15(2): 131-138
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.131
Published online Jan 14, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.131
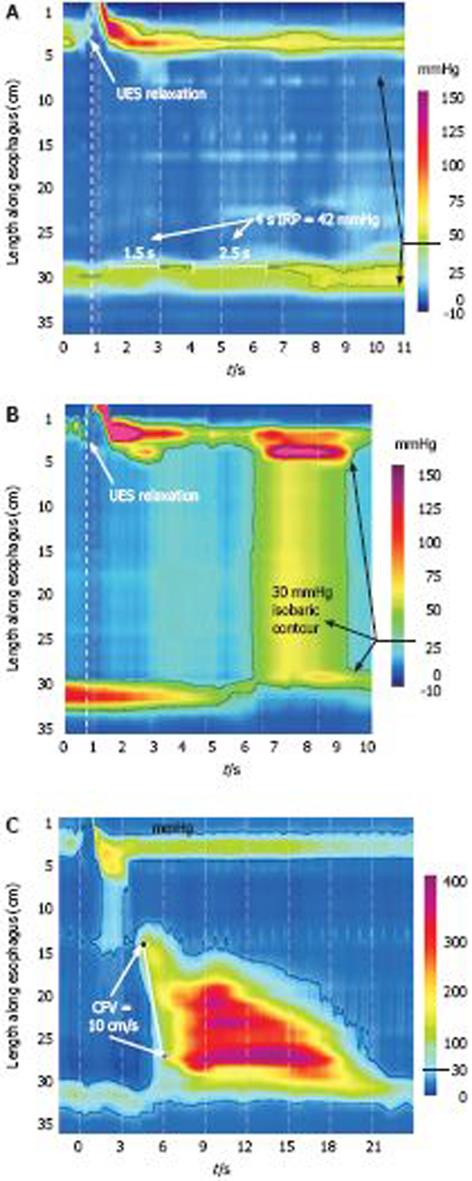
Figure 4 Achalasia subtypes based on manometric patterns of esophageal body contractility.
A: Classic achalasia. There is no significant pressurization within the body of the esophagus and there is concurrent impaired EGJ relaxation (IRP of 42 mmHg in this example);Achalasia subtypes based on manometric patterns of esophageal body contractility. B: Achalasia with compression. This subtype exhibits a rapid pan-esophageal pressurization;Achalasia subtypes based on manometric patterns of esophageal body contractility. C: Spastic Achalasia. Although this swallow is associated with rapidly propagated pressurization, the pressurization in this case is attributable to an abnormal lumen obliterating contraction. Modified from: Pandolfino et al[26].
- Citation: Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. New technologies in the gastrointestinal clinic and research: Impedance and high-resolution manometry. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(2): 131-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i2/131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.131