Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2008; 14(46): 7033-7058
Published online Dec 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.7033
Published online Dec 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.7033
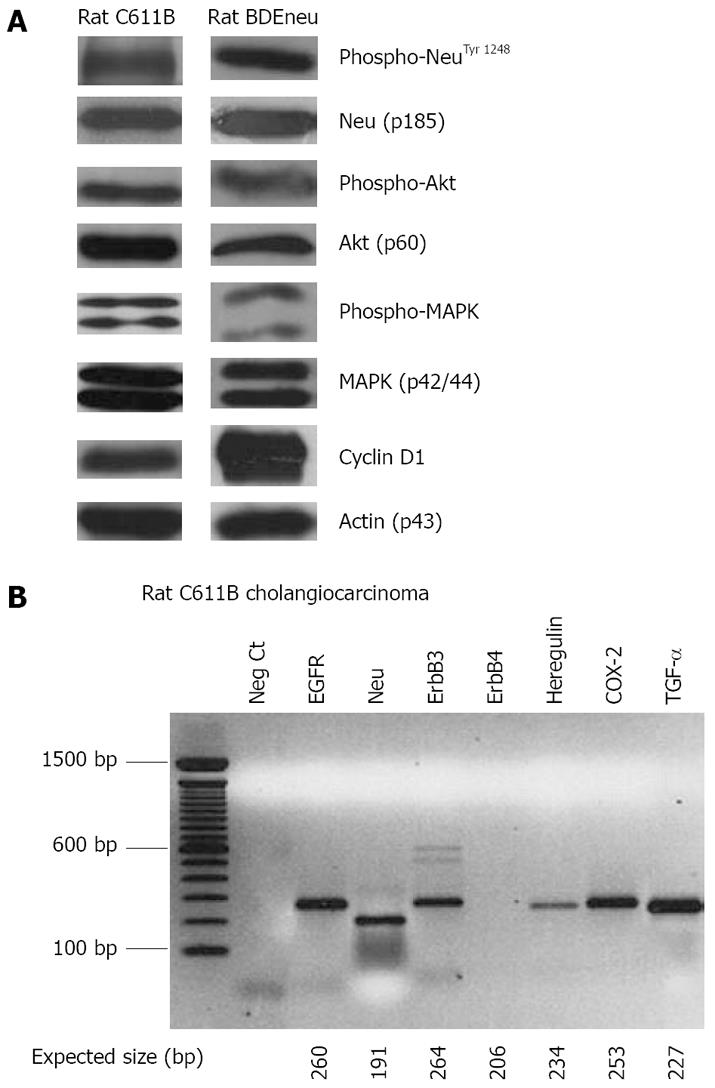
Figure 5 Western blot (A) and RT-PCR (B) analyses.
A: Relevant protein and phosphorylation profiles associated with aberrant Neu expression in rat C611B and BDEneu cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. C611B overexpress the wild-type c-neu gene[64], whereas BDEneu cells overexpress mutationally-activated neu oncogene[68,69]. Note that both cell lines are positive for phospho-Neu, phospho-Akt, and phospho-p42/44 MAPK, as well as show prominent expression of cyclin D1; B: RT-PCR analysis of c-erbB family receptor together with heregulin, TGF-α, and COX-2 mRNAs detected in malignant neoplastic ducts obtained by laser capture microdissection from a hepatic tumor formed in an isogenic Fischer 344 male rat following cell transplantation of rat C611B cholangiocarcinoma cells directly into liver. Note that as expected, among the ErbB family receptors, only ErbB4 mRNA is not detected in the tumor ducts. Moreover, it is also significant that mRNA signals for both the EGFR ligand TGF-α and for COX-2, which is known to be up-regulated in response to EGFR and/or Neu signaling, are each shown to be prominently detected in C611B cholangiocarcinoma.
- Citation: Sirica AE. Role of ErbB family receptor tyrosine kinases in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(46): 7033-7058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i46/7033.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.7033