Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2008; 14(25): 3937-3947
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3937
Published online Jul 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3937
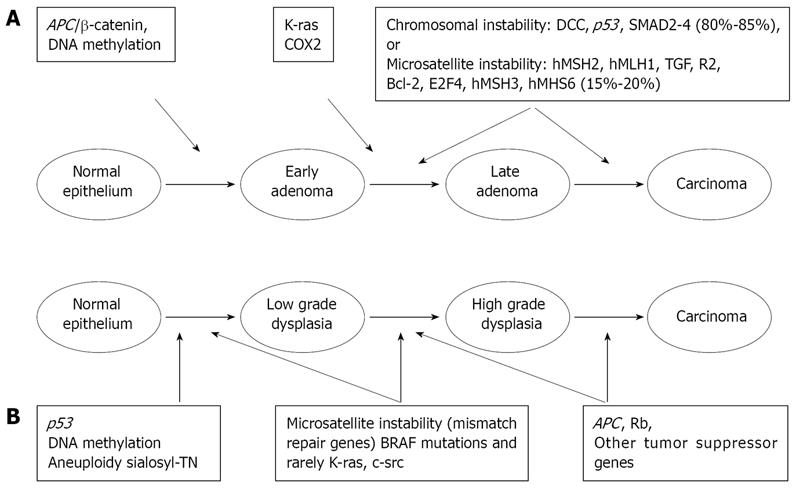
Figure 1 Summary of geneticalte-rations in sporadic colorectal cancer (A) and colitis-associated colorectal cancer (B).
The timing of p53 and APC mutations is different; unlike in sporadic neoplasia, mutations and LOH in p53 are early events in UC-associated CRCs. The opposite was reported for APC mutations[42].
- Citation: Lakatos PL, Lakatos L. Risk for colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: Changes, causes and management strategies. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(25): 3937-3947
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i25/3937.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3937