Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2008; 14(18): 2810-2817
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2810
Published online May 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2810
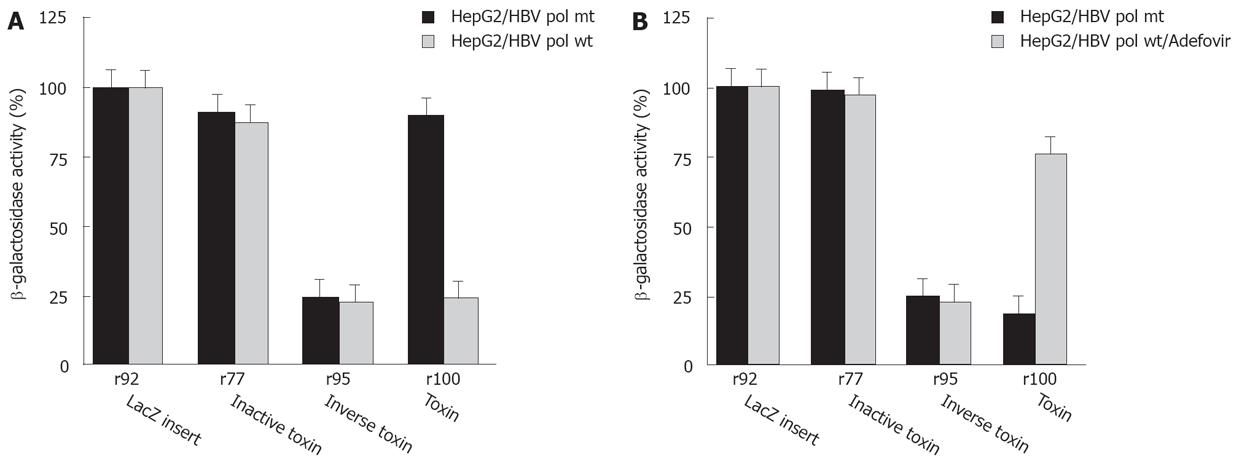
Figure 5 A: Cytotoxicity of toxin sense and antisense RNA to HepG2 cells in the presence or absence of transfected HBV polymerase expression plasmid.
The β-Gal activities obtained after cotransfection with the β-Gal expressing DNA plasmid p92 (7.5 &mgr;g), in vitro transcribed r92 control RNA (7.5 &mgr;g) and plasmids expressing either HBV harbouring a wild-type or mutant HBV polymerase (7.5 &mgr;g each) were set to 100%. Values resulting from coexpression of toxin RNAs (r77, r95, r100) with p92 and either wild-type HBV polymerase or mutant HBV polymerase expressing plasmids are expressed as relative levels. B: Cytotoxicity of toxin sense and antisense RNA to HepG2 cells in the presence or absence of 10 mmol/L adefovir. 7.5 &mgr;g RNA mixed with 7.5 &mgr;g p92 β-Gal expression plasmid were transfected in each experiment and β-Gal activities were quantified as described in legend to Figure 3. In addition, a wild-type HBV polymerase expression plasmid was transfected (7.5 &mgr;g). p92, control RNA from p92; p77, antisense RNA of inactivated toxin from p77; p95, sense toxin RNA from p95; p100, antisense RNA of active toxin from p100.
- Citation: Hafkemeyer P, Brinkmann U, Brinkmann E, Pastan I, Blum HE, Baumert TF. Pseudomonas exotoxin antisense RNA selectively kills hepatitis B virus infected cells. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(18): 2810-2817
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i18/2810.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2810