Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2007; 13(9): 1335-1346
Published online Mar 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1335
Published online Mar 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1335
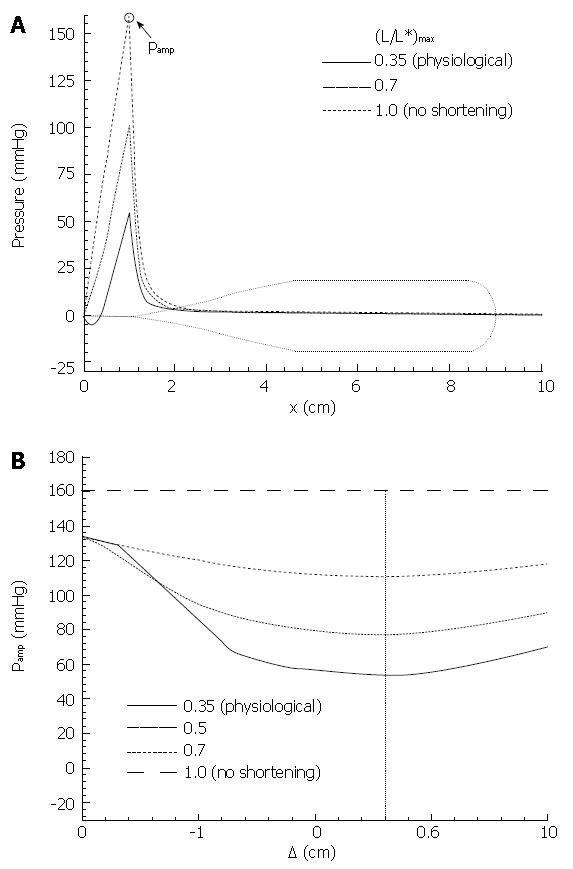
Figure 11 Primary result from Pal & Brasseur[18].
A: Mathematical model calculation of pressure during esophageal peristaltic transport with different levels of local longitudinal shortening, from the measured physiological level, to no shortening; B: Calculation of peak closure pressure as a function of separation △ between the circular muscle and longitudinal muscle contraction waves (Figure 10).
-
Citation: Brasseur JG, Nicosia MA, Pal A, Miller LS. Function of longitudinal
vs circular muscle fibers in esophageal peristalsis, deduced with mathematical modeling. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(9): 1335-1346 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i9/1335.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1335