Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2007; 13(7): 1060-1066
Published online Feb 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1060
Published online Feb 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1060
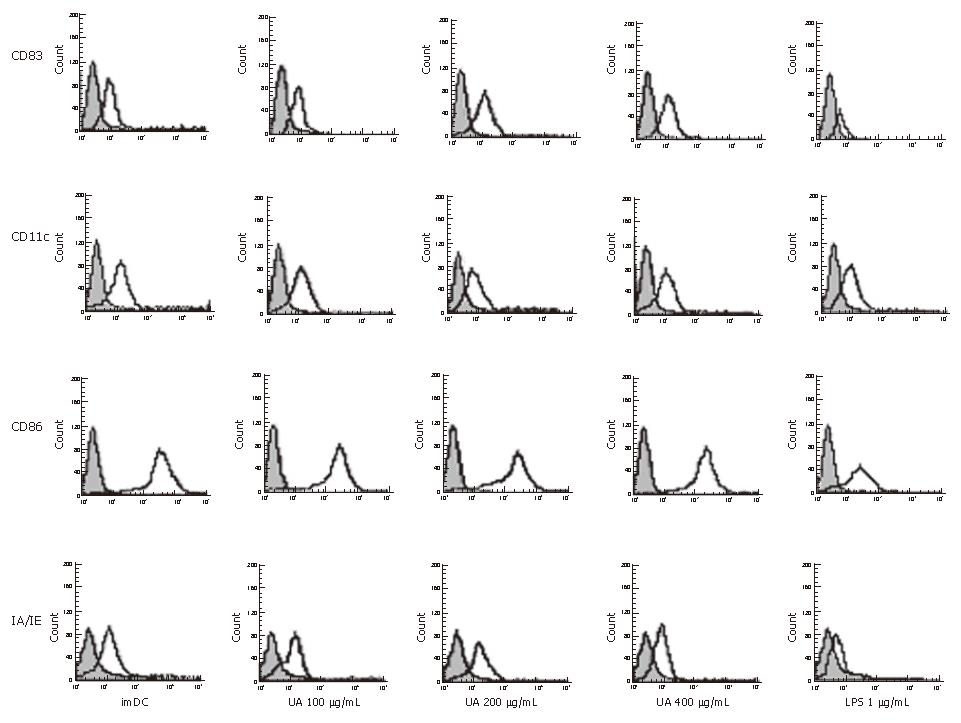
Figure 1 The cell surface markers analysis on dendritic cells by flow cytometry after exposure to uric acid or LPS.
Bone marrow-derived DCs were stimulated with 100, 200 and 400 μg/mL uric acid or 1 μg/mL LPS or Serum-free RPMI media 1640 for 48 h and immunostained with mAbs against CD11c, CD83, CD86 and IA/IE molecules (open histograms). Shade histograms represent the isotype control mAb staining of the cells. The histograms (Figure 1) and data (Table 1) are representative of five independent experiments.
- Citation: Ma XJ, Tian DY, Xu D, Yang DF, Zhu HF, Liang ZH, Zhang ZG. Uric acid enhances T cell immune responses to hepatitis B surface antigen-pulsed-dendritic cells in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(7): 1060-1066
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i7/1060.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1060