Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2007; 13(23): 3237-3244
Published online Jun 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3237
Published online Jun 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3237
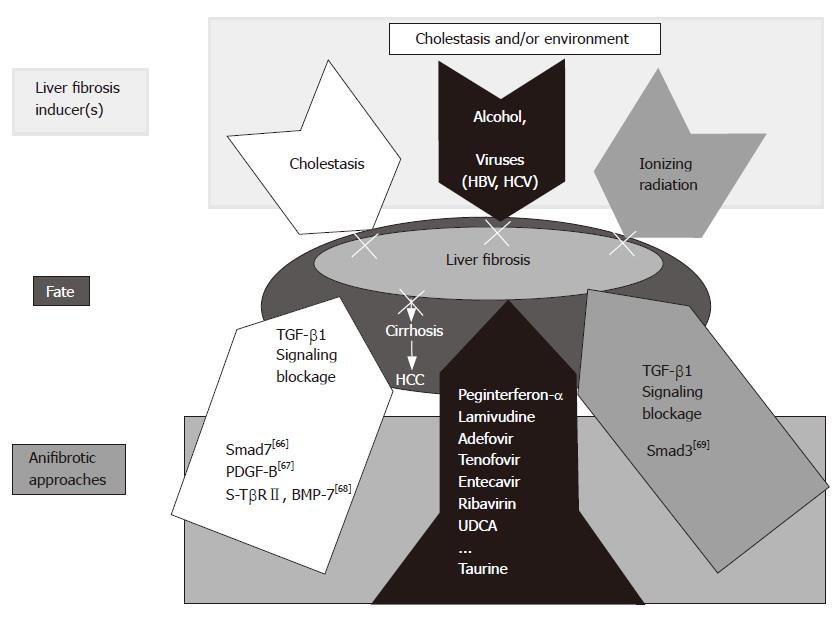
Figure 3 Working hypothesis: cause(s) and therapeutic alternatives for liver fibrosis.
In the present study, a combined peginterferon-α plus taurine treatment for fibrotic livers was applied successfully. Though different etiologies are responsible for chronic liver diseases, viruses and alcohol prevail worldwide. Our results can represent a therapeutic option to prevent progression of the underlying disease to fibrosis in the liver. Other experimental models are also presented including TGF-β1 signaling blockage by Smad7 overexpression[66], PDGF-B[67], and a soluble receptor TGF-β2 (TβRII) and BMP-7[68]. Liver fibrosis affected by ionizing radiation can be inhibited by Smad knock out [Smad3 (-)][69].
- Citation: Tasci I, Mas MR, Vural SA, Deveci S, Comert B, Alcigir G, Mas N, Akay C, Bozdayi M, Yurdaydin C, Bozkaya H, Uzunalimoglu O, Isik AT, Said HM. Pegylated interferon-alpha plus taurine in treatment of rat liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(23): 3237-3244
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i23/3237.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3237