Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2007; 13(17): 2467-2478
Published online May 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2467
Published online May 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2467
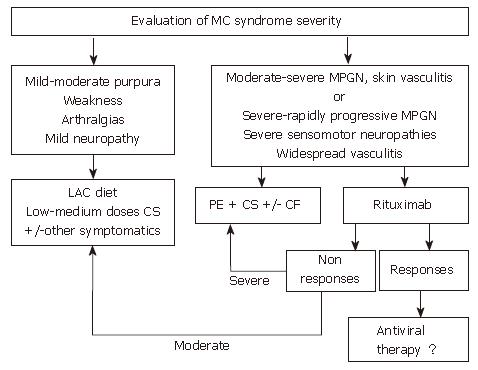
Figure 3 Algorithm for treatment of HCV-positive mixed cryoglobulinemia patients who are non-responders or in whom antiviral treatment is contraindicated or not tolerated.
When antiviral treatment is not indicated this algorithm suggests other approaches for the management of mixed cryoglobulinemia, including anti-inflammatory drugs (first corticosteroids, CS), procedures able to lower the concentration of cryoglobulins such as the low antigen content (LAC) diet or plasma exchange (PE) as well as immunosuppressive drugs (cyclophosphamide, CF). In patients with only mild to moderate syndrome, cycles of therapy with anti-inflammatories, the LAC diet or other symptomatic treatments are suggested. Therapy should be adapted to the single patient and limited in time. In patients with more severe syndromes, cycles of plasma exchange plus corticosteroids and/or immunosuppressive drugs are indicated. The use of rituximab, a selective B-cell suppressor, may be an alternative treatment in some cases where antiviral therapy is initially contraindicated. (Zignego AL, Postgraduate Course EASL 2006, Vienna and [34])
- Citation: Zignego AL, Giannini C, Ferri C. Hepatitis C virus-related lymphoproliferative disorders: An overview. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(17): 2467-2478
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i17/2467.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2467