Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2005; 11(29): 4511-4518
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4511
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4511
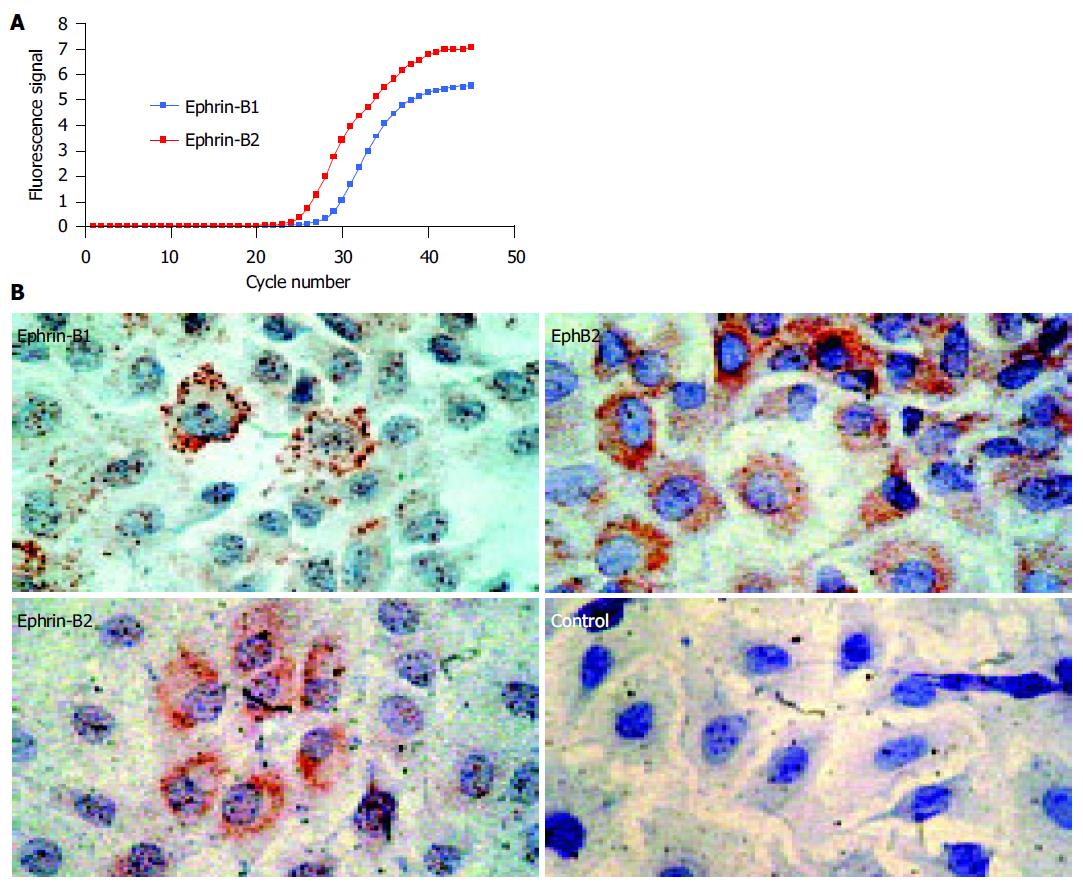
Figure 1 Rat IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells express ephrin-B ligands on the mRNA and protein level.
A: Real-time RT-PCR shows expression of ephrin-B1 and -B2 mRNA. As the curve of ephrin-B2 demonstrates lower CT-values, the amount of ephrin-B2 mRNA starting material was higher than the amount of ephrin-B1 mRNA. The values were normalized by detection of the 18S rRNA (data not shown); B: IEC-6 cells coexpress ephrin-B1/2 and the corresponding EphB2 receptor on the protein level. IEC-6 cells may therefore be able to interchange cell-cell signals via EphB2/ephrin-B1/2 contacts. The coexpression of the EphB2 receptors and ephrin-B1/2 ligands is in accordance with previous data on human adult intestinal tissue in these cells[11].
- Citation: Hafner C, Meyer S, Hagen I, Becker B, Roesch A, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Ephrin-B reverse signaling induces expression of wound healing associated genes in IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(29): 4511-4518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i29/4511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4511