Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2005; 11(26): 4024-4031
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4024
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4024
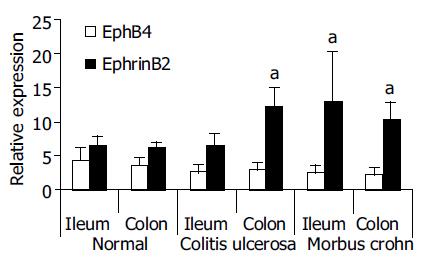
Figure 2 Differential gene expression of Eph-RTKs and ephrins in the mucosa of IBD patients (TaqMan® RT-PCR validation of Affymetrix® cDNA array results[17]).
Individual RNAs from perilesional total mucosa biopsies (ileum terminale and colon) of 4 control subjects, 4 MC patients and 4 CU patients were analyzed. Real-time RT-PCR confirmed significant up-regulation of ephrin-B2 in MC patients (ileum and colon) and CU (colon). Differential expression of EphB4, as suggested by the Affymetrix® array data, was not significant. The relative expression values were calculated according to the standard curve method of the TaqMan® protocol (Applied Biosystems, Darmstadt, Germany) by normalization with a housekeeper gene (18S rRNA) and are therefore unitless (for details, see[15]). aP < 0.05 vs normal.
- Citation: Hafner C, Meyer S, Langmann T, Schmitz G, Bataille F, Hagen I, Becker B, Roesch A, Rogler G, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Ephrin-B2 is differentially expressed in the intestinal epithelium in Crohn’s disease and contributes to accelerated epithelial wound healing in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(26): 4024-4031
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i26/4024.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4024