Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2016; 22(16): 4168-4182
Published online Apr 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i16.4168
Published online Apr 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i16.4168
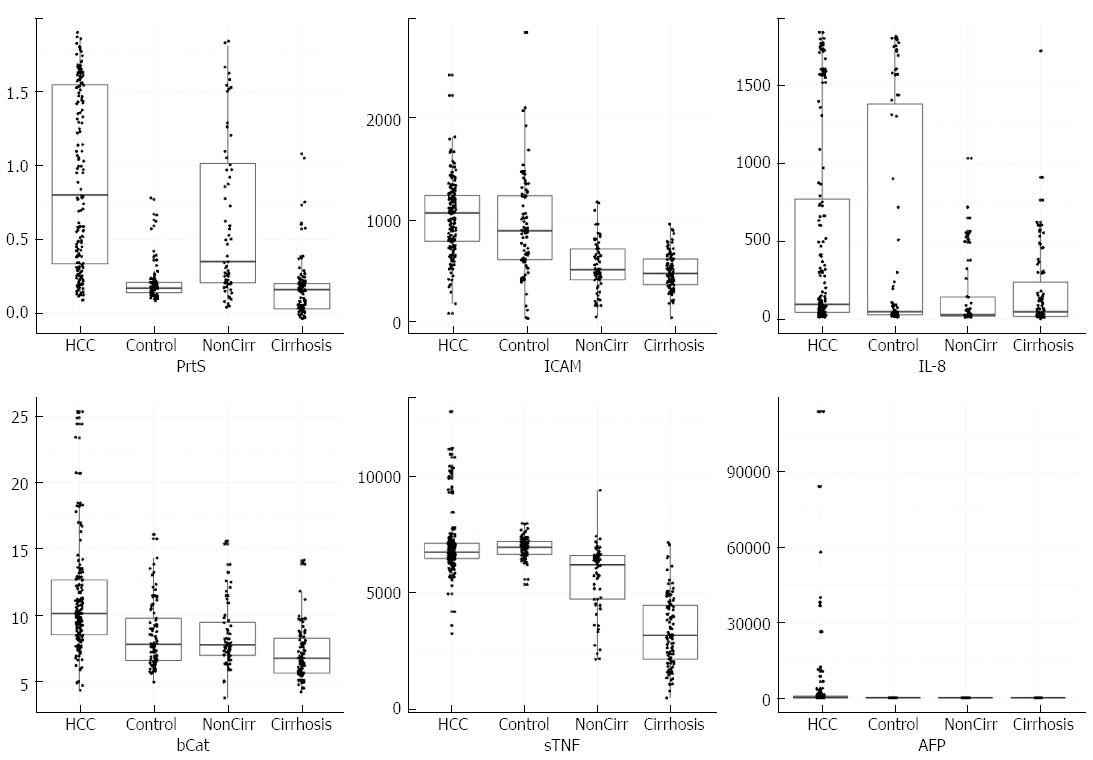
Figure 1 Box plots with scattered measurement points showing distribution of measured serum markers levels in different investigated groups.
Sample groups on x axis and protein concentrations on Y axis. The markers from left to right are proteosome (PrtS), ICAM (sICAM-1), IL-8, β-catenin (bCat), sTNF-RII (sTNF), and AFP. The box defines the boundaries of the first and third quartiles of data and the median values are indicated by horizontal lines within the boxes.
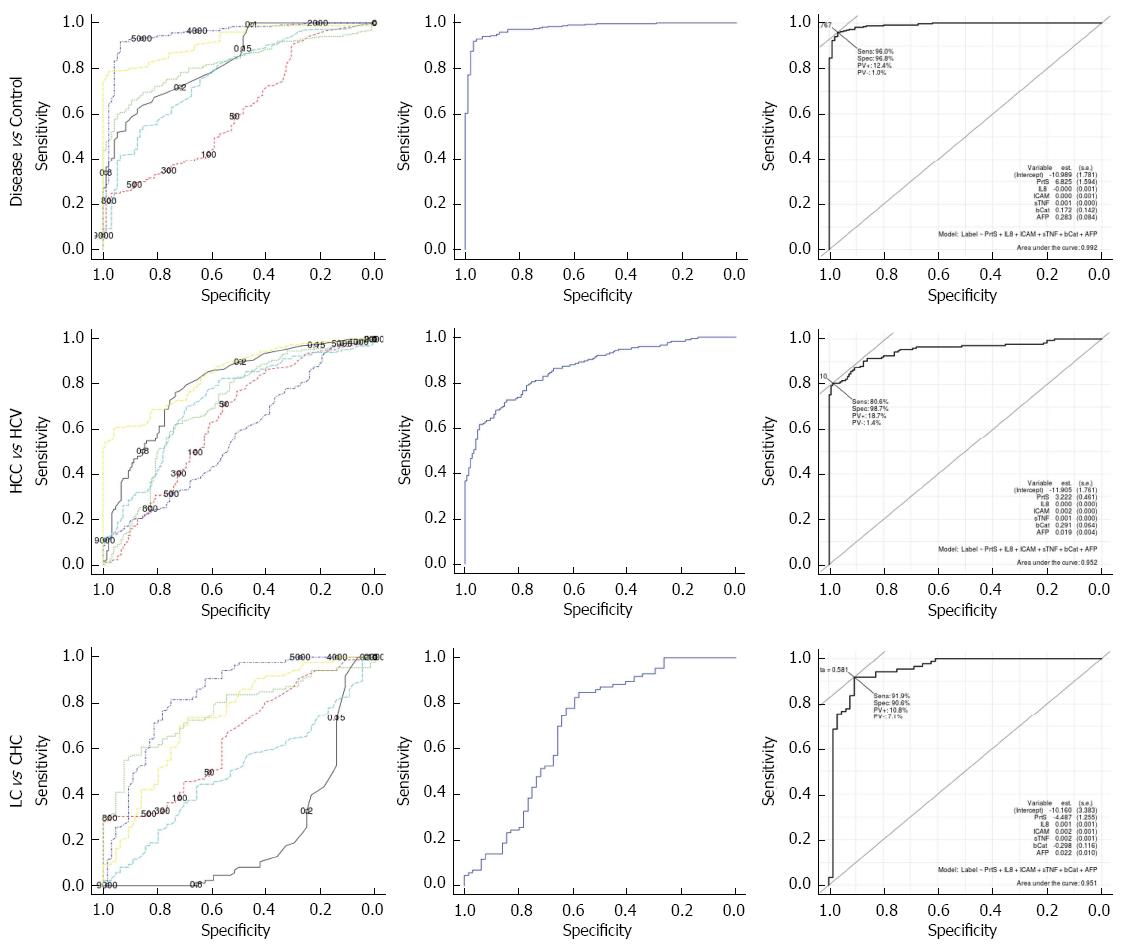
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic curves for the three pairwise comparisons of investigated groups used in our algorithm.
The leftmost column includes receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for individual markers, The middle columns includes ROC curves for Method 1 based on for the multi-class classifier, and the rightmost column includes ROC curves for Method2 based on binary class classifiers. On the ROC curve of Method 2, we depict the respective model and appropriate cut-offs. The different ROC curves for proteasome, IL-8, sICAM-1, sTNF-RII, β-catenin, and AFP in the leftmost column are colored black, red, green, blue, cyan, and yellow, respectively. Prts: Proteasome.
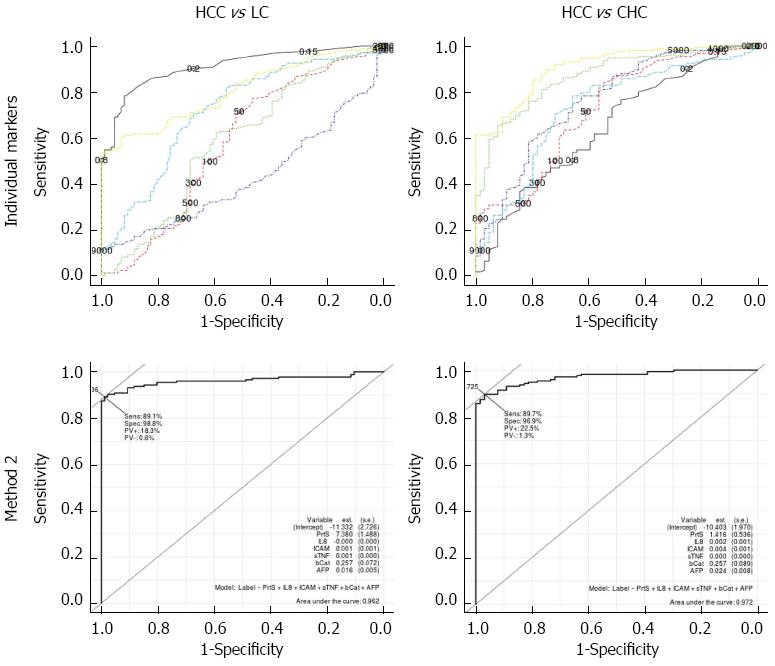
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curves of individual markers vs Method 2 (based on binary class-calssifier) over different pairwise comparisons discriminating hepatocellular carcinoma groups from liver cirrhosis group and chronic hepatitis C group.
CHC: Chronic hepatitis C; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
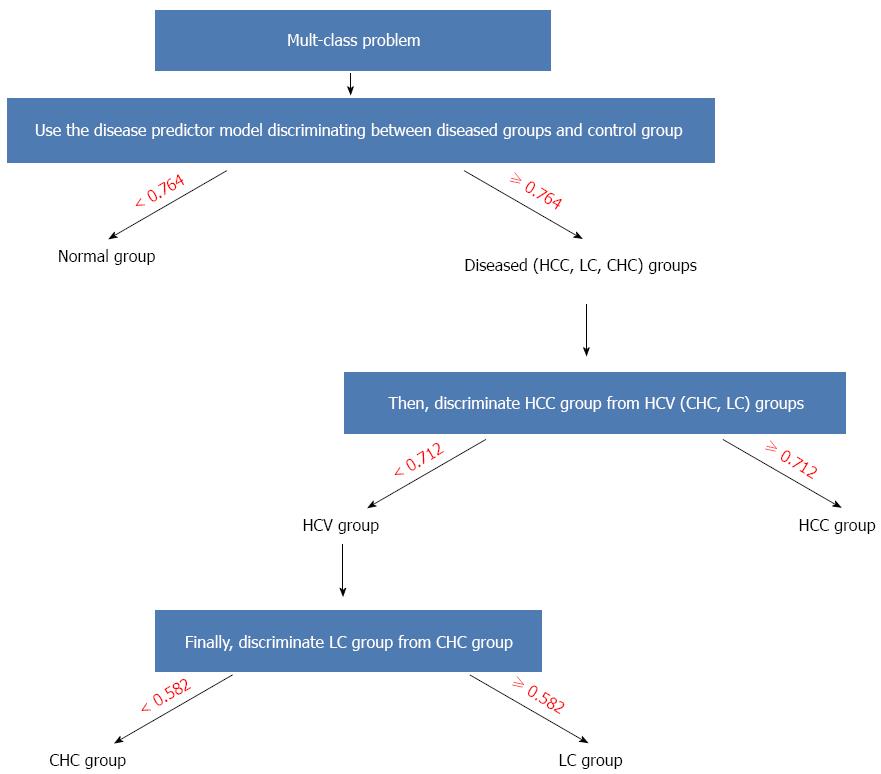
Figure 4 Algorithm of the disease predictor model for identifying muti-class problem.
Each discrimination step in the algorithm has its own mathematical model with the appropriate cutoff that was conceived from Table 7. CHC: Chronic hepatitis C; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
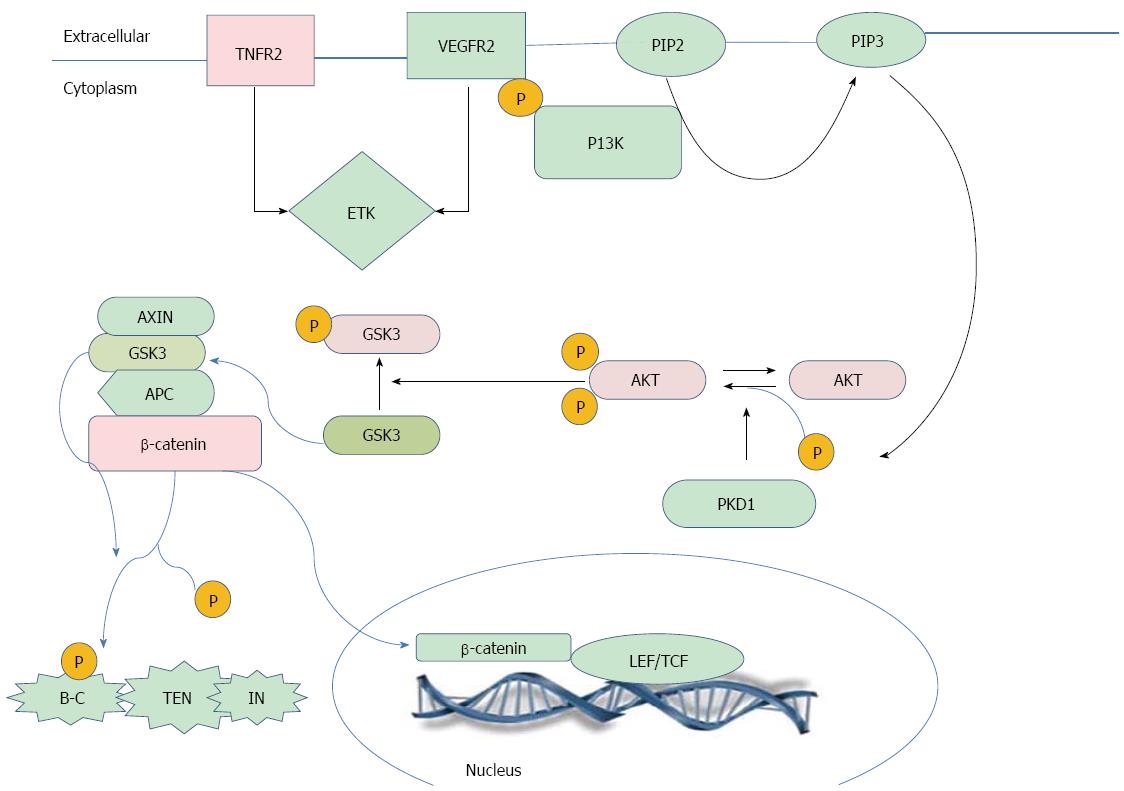
Figure 5 The hypothetical mechanism between tumor necrosis factor receptor II and β-catenin.
TNF-RII: Tumor necrosis factor receptor II.
- Citation: Zekri ARN, Youssef ASED, Bakr YM, Gabr RM, Ahmed OS, Elberry MH, Mayla AM, Abouelhoda M, Bahnassy AA. Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma co-occurring with hepatitis C virus infection: A mathematical model. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(16): 4168-4182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i16/4168.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i16.4168